Tooth Decay: 20 Essential Questions Answered for a Healthier Smile
Tooth decay is one of the most widespread dental issues globally, quietly affecting millions of people across all age groups. From a child’s first cavity to an adult’s painful root canal, tooth decay can have serious consequences when ignored—but it’s also highly preventable.
If you’ve ever wondered what those white spots on your teeth mean, how sugar actually causes cavities, or whether tooth decay runs in families, you’re not alone. This guide answers 20 of the most common and important questions about tooth decay, empowering you with the knowledge you need to protect your smile for life.
what Is Tooth Decay?
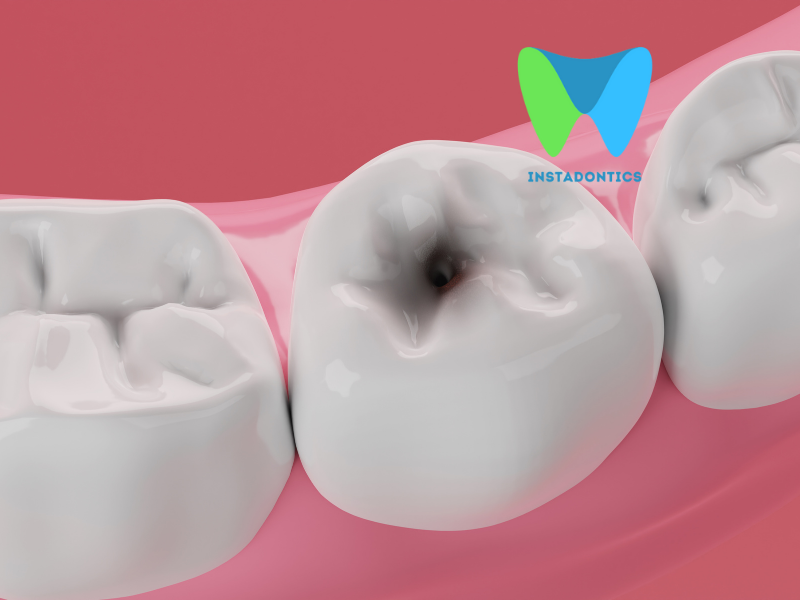
Tooth decay—also known as dental caries or cavities—is the gradual breakdown of a tooth’s outer layer (enamel) caused by acid-producing bacteria. When you eat, bacteria in your mouth feed on sugars and starches, producing acid that slowly wears down the enamel. Over time, this leads to cavities, sensitivity, and deeper dental damage if left untreated.
✅ 20 Key Questions About Tooth Decay (With Straightforward Answers)
Q1: What are the early signs of tooth decay?
Early signs of decay often go unnoticed because they may not cause immediate pain. The most common early indicators include white spots on the enamel, which suggest mineral loss. Mild sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods is another sign, especially if it’s a new sensation. If caught early, these symptoms can be managed and the damage reversed with the right care.
Q2: Can tooth decay be reversed?
Yes, early-stage tooth decay—before a cavity has formed—can often be reversed. This is typically done through fluoride treatments, good oral hygiene, and dietary changes. Fluoride helps remineralize enamel and repair early damage. However, once a hole forms in the tooth, professional treatment like a filling is necessary.
Q3: How often should I visit the dentist?
Most dental professionals recommend seeing your dentist every six months for a routine checkup and cleaning. These visits help detect early signs of tooth decay before they progress. People with a history of frequent cavities, gum disease, or other dental issues may need more frequent appointments based on individual risk factors.
Q4: Is tooth decay contagious?
Tooth decay itself isn’t contagious, but the bacteria that cause it—especially Streptococcus mutans—can be passed from person to person through saliva. This means sharing utensils, kissing, or blowing on a child’s food can spread cavity-causing bacteria. Practicing good hygiene can reduce this risk.
Q5: What foods should I avoid to prevent tooth decay?
Avoid foods high in added sugars, such as candy, cookies, and soda, as these feed harmful oral bacteria. Starchy snacks like chips and crackers can also stick to teeth and promote decay. Acidic drinks like fruit juice or sports drinks can erode enamel, especially when consumed frequently or sipped over time.
Q6: Are there any home remedies for tooth decay?
While home care can’t reverse advanced decay, it can slow or stop early-stage damage. Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing helps remove plaque and prevent progression. Rinsing with a fluoride mouthwash and chewing xylitol gum can support enamel remineralization and reduce bacterial activity.
Q7: How do I know if I have a cavity?
Common symptoms of a cavity include toothache, sensitivity to temperature or sweets, and visible holes or dark spots on the teeth. Some cavities may cause pain when biting down. However, not all cavities cause symptoms in the early stages, so regular dental exams are essential for early detection.
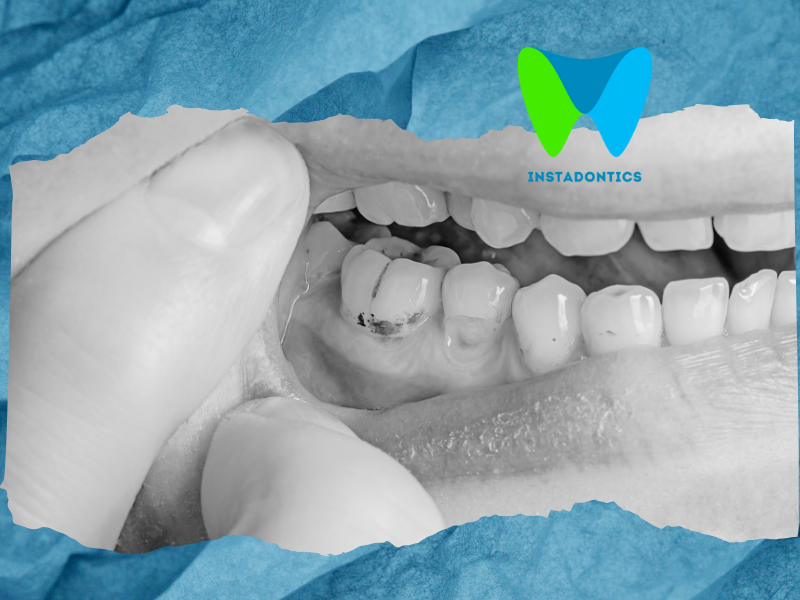
Q8: What happens if tooth decay is left untreated?
If decay isn’t treated, it can spread deeper into the tooth, affecting the dentin and pulp. This can result in severe pain, infection, or even an abscess. Over time, untreated decay can destroy the tooth, requiring root canal therapy or extraction. In some cases, dental infections can affect overall health.
Q9: Can tooth decay cause bad breath?
Yes, decay can lead to persistent bad breath (halitosis). Bacteria that break down food particles in decayed areas release foul-smelling gases. Infections associated with advanced decay or abscesses can further worsen odor, making good oral hygiene and dental treatment essential.
Q10: Are some people more prone to tooth decay?
Yes, individual risk factors include genetics, enamel strength, diet, saliva production, and oral hygiene habits. Some people naturally have more acidic mouths or more cavity-prone bacteria. Medical conditions like dry mouth, diabetes, or acid reflux can also increase decay risk.
Q11: How is tooth decay different from gum disease?
Tooth decay involves the breakdown of tooth enamel and structure due to acids from bacteria. Gum disease (like gingivitis or periodontitis), on the other hand, affects the gums and bone supporting the teeth. While both are caused by plaque, they target different parts of the mouth and require different treatments.
Q12: Can tooth decay affect my overall health?
Yes. Untreated dental infections can spread to the bloodstream and contribute to systemic health issues, including heart disease, respiratory infections, and complications in diabetes or pregnancy. Oral health is closely linked to general health and well-being.
Q13: Is tooth decay hereditary?
Genetics can influence your susceptibility to tooth decay, including enamel hardness, saliva composition, and immune response. However, lifestyle and oral care habits play a much bigger role in whether cavities actually develop. Good hygiene can often overcome genetic predispositions.
Q14: Can tooth decay lead to tooth loss?
Absolutely. When decay destroys a significant portion of the tooth structure, the tooth can no longer function and may need to be extracted. Severe decay can also compromise surrounding tissues and increase the risk of tooth mobility and eventual loss.
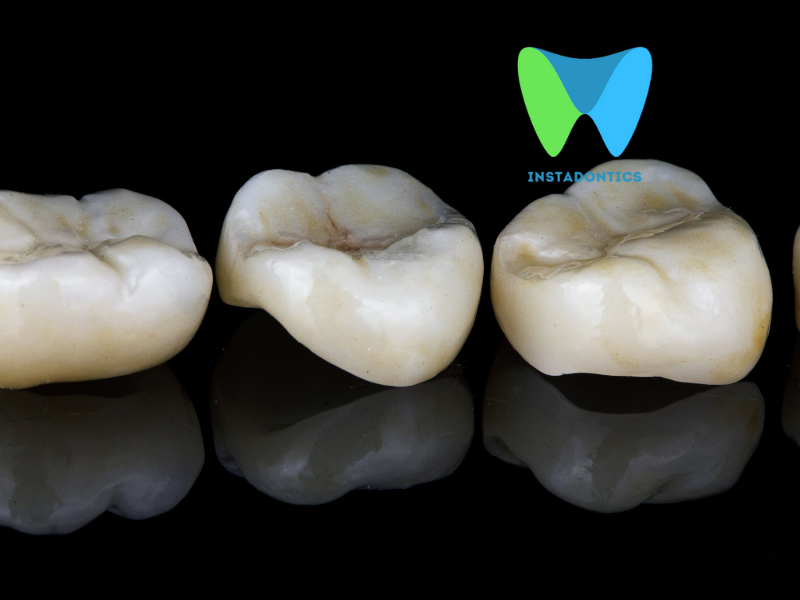
Q15: How do dentists treat tooth decay in children?
Treatment depends on the severity of the decay. Options include fluoride varnishes for early lesions, fillings for cavities, and stainless steel crowns for larger restorations. Education on brushing, flossing, and nutrition is key to preventing recurrence and building lifelong habits.
Q16: Can adults get tooth decay?
Yes, and adults are particularly at risk for root decay as gums recede with age. This exposes softer root surfaces that decay more easily. Older adults taking medications that cause dry mouth are especially vulnerable to decay due to reduced saliva.
Q17: How do I choose the right toothpaste to prevent tooth decay?
Look for toothpaste containing fluoride, which strengthens enamel and reduces acid damage. Products with the ADA Seal of Acceptance have been tested for safety and effectiveness. If you have sensitivity, dry mouth, or specific needs, your dentist can recommend a specialized option.
Q18: What is the best way to floss to prevent tooth decay?
Flossing removes plaque and food particles from between teeth where a toothbrush can’t reach. Use a gentle back-and-forth motion, curve the floss around each tooth in a “C” shape, and clean just under the gumline. Consistent, proper technique is more important than the tool you use.
Q19: How does sugar cause tooth decay?
Sugar feeds the bacteria in dental plaque, allowing them to produce acid as a byproduct. This acid dissolves minerals in the enamel, creating weak spots that develop into cavities over time. Frequent sugar intake keeps the mouth in an acidic state, increasing the risk of decay.
Q20: What are the latest advancements in the treatment of tooth decay?
New developments include resin infiltration (e.g., ICON therapy) for early lesions, laser-based cavity detection, and bioactive filling materials that release fluoride or calcium. Research into caries vaccines and remineralization therapies using nanotechnology is also advancing rapidly.
Final Thoughts: Knowledge is Your Best Defense
Tooth decay is common—but it’s not inevitable. Armed with the right information, you can take action early, reverse early damage, and prevent future cavities altogether. That starts with regular dental visits, smart oral hygiene, a balanced diet, and awareness of the signs.
If you’re unsure about a spot on your tooth or experiencing pain, don’t wait—your dentist is your partner in keeping your smile strong and healthy.
Read more about the causes of tooth decay.
Understanding tooth decay and its causes, symptoms, and treatments is essential for maintaining good oral health. By practicing proper oral hygiene, making dietary changes, and visiting the dentist regularly, you can prevent and manage tooth decay effectively.