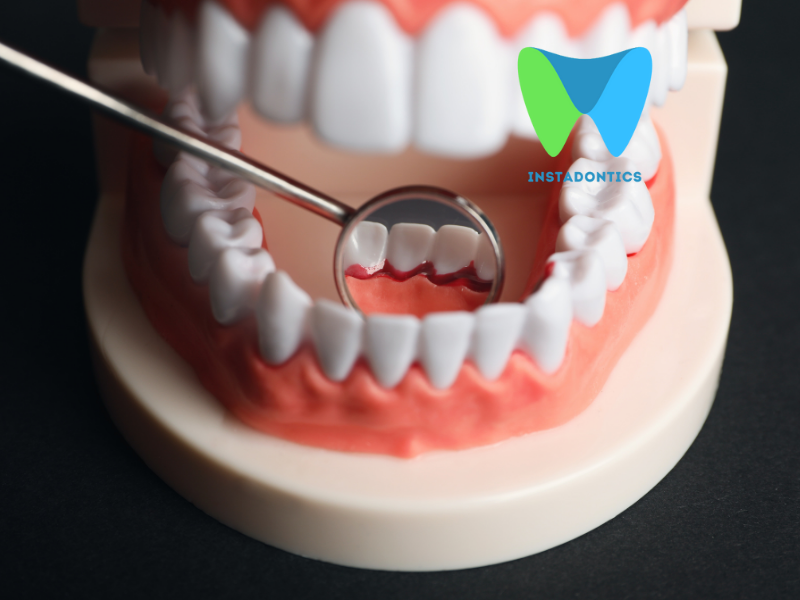
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a prevalent yet preventable condition affecting the gum tissues and bone that support your teeth. Though often underestimated, gum disease can have serious implications for oral health and overall well-being. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about gum disease, from symptoms and causes to prevention and treatment.
The Importance of Gum Health
Before diving into the specifics of gum disease, it’s crucial to understand the importance of maintaining healthy gums. Healthy gums serve as the foundation of a beautiful smile and are pivotal in preventing tooth loss. Ignoring gum health can lead to significant dental issues and even impact systemic health, including increasing the risk for conditions like heart disease and diabetes.
What is Gum Disease?
Gingivitis: The Early Stage
Gum disease typically begins with gingivitis, an inflammation of the gums. Gingivitis is characterized by redness, swelling, and bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing. At this stage, the damage is usually reversible with proper oral hygiene practices.
Periodontitis: The Advanced Stage
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis. In this more severe form, the inner layer of the gum and bone pull away from the teeth, forming pockets. These pockets can collect debris and become infected. Without timely intervention, periodontitis can lead to tissue and bone loss and ultimately tooth loss.
Causes of Gum Disease
Several factors contribute to the onset of gum disease:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to form on the teeth.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: These habits significantly increase the risk of gum disease.
- Genetics: A family history of dental problems can predispose individuals to gum disease.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in women, can make gums more sensitive and vulnerable to disease.
- Medications: Certain drugs can reduce the flow of saliva, making it easier for plaque to build up.
- Health Conditions: Diseases like diabetes can affect the body’s ability to fight infection, including infections in the gums.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
Recognizing the symptoms of gum disease early can lead to prompt treatment and better outcomes. Key symptoms include:
- Swollen, red, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums during or after brushing
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums or longer-looking teeth
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Painful chewing
The Impact of Gum Disease on Overall Health
Gum disease is not just an oral health issue; it has systemic implications as well. Chronic inflammation from gum disease has been linked to various health conditions, including:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Poor gum health can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Diabetes: There is a bi-directional relationship between diabetes and gum disease, where each condition can exacerbate the other.
- Pregnancy Complications: Gum disease has been linked to premature birth and low birth weight in newborns.
- Respiratory Infections: Bacteria from infected gums can be inhaled into the lungs, leading to infections such as pneumonia.
Preventing Gum Disease
The Role of Oral Hygiene
Good oral hygiene is the cornerstone of preventing gum disease. This includes:
- Brushing Twice Daily: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to brush your teeth thoroughly.
- Daily Flossing: Flossing removes plaque and food particles between teeth and along the gum line.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Professional cleanings and checkups help detect early signs of gum disease.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease:
- Quit Smoking: This is one of the most effective ways to improve gum health.
- Balanced Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall health and gum health.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps wash away food particles and bacteria.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
Non-Surgical Treatments
For early-stage gum disease, non-surgical treatments can be very effective:
- Professional Cleaning: Removing plaque and tartar buildup can help reverse gingivitis.
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep-cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line.
Surgical Treatments
In more advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary:
- Flap Surgery: This involves lifting back the gums to remove tartar and then stitching the gums back in place.
- Bone and Tissue Grafts: These procedures use natural or synthetic materials to regenerate lost bone and tissue.
When to See a Dentist
It’s crucial to consult a dentist at the first sign of gum disease. Regular dental visits can help catch gum disease in its early stages and prevent more severe health issues down the line.
FAQ on Gum Disease
What are the first signs of gum disease?
The early signs of gum disease include red, swollen gums that bleed easily, especially during brushing or flossing.
Can gum disease be reversed?
Yes, early-stage gum disease (gingivitis) can often be reversed with proper oral hygiene and professional dental cleanings. However, once gum disease progresses to cause bone loss (loss of the bone supporting the teeth) it cannot be reversed. Proper treatment prevents the advancement of gum disease.
Is gum disease painful?
Gum disease is not always painful, especially in its early stages. However, advanced gum disease can cause discomfort while chewing, sensitivity, and loose teeth.
How can I prevent gum disease?
Brushing and flossing daily, avoiding tobacco, eating a balanced diet, and regular dental checkups are effective ways to prevent gum disease.
Does gum disease affect overall health?
Yes, gum disease has been linked to several systemic conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections.
Can children get gum disease?
While gum disease is more common in adults, children and teenagers can also develop it, especially the early stage known as gingivitis.
Are there any home remedies for gum disease?
Home remedies like saltwater rinses can help reduce inflammation, but professional dental treatment is essential for effectively managing gum disease.
Gum disease is a serious but often preventable condition. Maintaining good oral hygiene, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and regular dental visits are key to keeping your gums healthy. If you suspect you have gum disease, seek professional dental care promptly to prevent further complications. Your gums are the foundation of a healthy smile—take care of them!
If you need comprehensive dental care or advice on gum disease, don’t hesitate to schedule an appointment with your dentist today.