Dental health is often taken for granted until a significant problem arises. One such problem is a dental infection, which can escalate into a life-threatening situation if not properly managed. This article dives into the critical issue of dental infections, providing you with a deep understanding of how serious they can become, how quickly they can escalate, and the steps you can take to prevent such a dire outcome.
The Silent Threat of Dental Infections
Imagine a small problem in your mouth turning into a life-threatening issue. While this may seem far-fetched, dental infections can escalate rapidly if left untreated. Understanding the seriousness of dental infections and the timeline for potential lethal outcomes is essential for everyone who values their health. In this article, we’ll explore how long it can take for a dental infection to kill you, the stages of infection, and preventive measures to protect your health.
What is a Dental Infection?
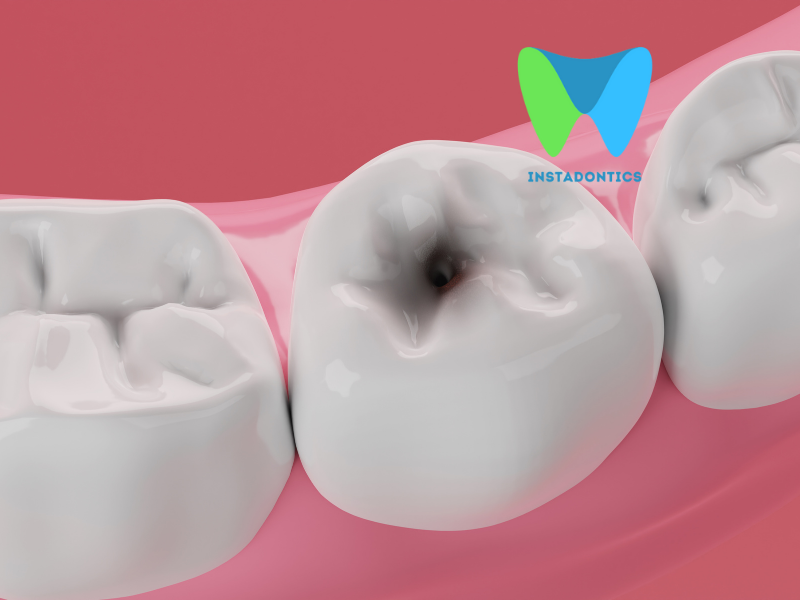
A dental infection, also known as a tooth abscess, occurs when bacteria invade the innermost part of the tooth, known as the pulp. This infection leads to the accumulation of pus and can cause severe pain, swelling, and even fever. Left untreated, it can spread to other parts of the body and become life-threatening.
Types of Dental Infections
1. Periapical Abscess
This type of abscess forms at the tip of a tooth’s root when bacteria enter through a cavity, crack, or chip and infect the pulp (the innermost part of the tooth containing nerves and blood vessels). The body responds by sending white blood cells to the site, leading to a buildup of pus and pressure. If untreated, the infection can spread to surrounding tissues and bones.
2. Periodontal Abscess
This abscess occurs in the gums next to a tooth root and is often associated with advanced gum disease (periodontitis). It typically results from an infection in the deep pockets between the tooth and gums. This type of abscess can cause swelling, bleeding, and eventually lead to bone and tooth loss.
3. Gingival Abscess
A gingival abscess is limited to the gum tissue and does not involve the tooth or periodontal ligament. It is usually caused by food particles or foreign objects (like popcorn kernels) becoming trapped in the gums, leading to localized infection and swelling. These are typically less severe but still require treatment to avoid progression.
How Does a Dental Infection Spread?
Initial Stages
When bacteria reach the tooth pulp, the body responds with inflammation and sends white blood cells to fight the infection. This initial stage causes intense pain and can make chewing or opening your mouth difficult.
Advanced Stages
If not treated, the infection can spread from the tooth to the surrounding tissues, jawbone, and even the bloodstream. This progression can lead to a condition known as sepsis, a life-threatening response to infection.
Timeline of a Dental Infection Turning Deadly
Initial Symptoms
In the early stages, symptoms include:
- Severe toothache
- Swelling in the gums
- Sensitivity to hot and cold
- Fever
Escalation
Increased Swelling
The swelling can spread from the gums to the face, neck, or jaw. In severe cases, it can impair your ability to open your mouth or speak.
Difficulty Swallowing or Breathing
This is a red flag indicating the infection may be spreading to deeper tissues or even the airway. It constitutes a medical emergency.
Pus Discharge
Pus may drain from the abscess into the mouth, sometimes leaving a foul taste or odor.
High Fever
A spike in body temperature is a strong indication that the infection is no longer localized and could be affecting your overall health.
Life-Threatening Stage
If left untreated, the infection can spread to vital areas such as:
Jawbone Infection (Osteomyelitis)
If bacteria reach the jawbone, they can cause inflammation and destruction of bone tissue, leading to chronic pain, swelling, and possibly jaw fractures.
Sinus Infection (Sinusitis)
Infections in upper teeth can spread into the sinus cavities, causing headaches, nasal congestion, facial pain, and chronic drainage.
Brain Abscess
A rare but deadly complication, this occurs when the infection spreads through the bloodstream or surrounding tissues into the brain, potentially leading to seizures, loss of consciousness, or death.
Sepsis
This is the body’s extreme response to infection, causing systemic inflammation and potentially leading to organ failure and death. Immediate hospitalization and aggressive treatment are necessary.
Here’s a more detailed and reader-friendly version of the “When to Seek Emergency Help” section, expanding on each sign and explaining why it’s critical:
When to Seek Emergency Help
Dental infections can escalate quickly, and knowing when to get emergency care can save your life. While some symptoms may seem manageable at first, others signal that the infection may be spreading beyond your tooth and into surrounding tissues or even your bloodstream.
Recognizing the Warning Signs
If you experience any of the following symptoms, do not delay—seek emergency medical or dental care immediately:
1. Persistent or Severe Tooth Pain
Ongoing, intense tooth pain—especially if it’s throbbing and doesn’t subside with over-the-counter medications—could indicate a deep infection that may soon spread to nearby tissues. Pain that keeps you awake at night or worsens when lying down should never be ignored.
2. Swelling in the Mouth, Jaw, or Face
Swelling that starts in your gums or cheeks and begins to spread outward is a red flag. It may indicate that pus is accumulating, and the infection is extending into the surrounding soft tissues. This can progress rapidly and compromise nearby structures.
Dangerous Signs of a Spreading Infection
These symptoms suggest that the dental infection is moving into critical areas of the body and may become life-threatening:
3. Difficulty Breathing or Swallowing
If swelling spreads toward the throat, it can press on the airways or esophagus, making it hard to breathe or swallow. This could mean the infection is entering the deep spaces of the neck—a serious condition known as Ludwig’s Angina, which requires immediate hospitalization.
4. High or Persistent Fever
A fever above 101°F (38.3°C), especially if it doesn’t come down with medication, suggests the body is fighting a systemic infection. If the fever is accompanied by chills or sweating, it may indicate the onset of sepsis—a potentially deadly response to infection that can lead to organ failure.
5. Swelling Affecting Your Face, Neck, or Eyes
Swelling that reaches the eyes or travels down the neck suggests that the infection is no longer localized. This may impact your vision, breathing, or ability to open your mouth (trismus). If left untreated, the infection can reach the bloodstream or the brain.
Additional Emergency Symptoms Include:
- Fatigue or confusion (possible signs of sepsis)
- Rapid heart rate or breathing
- Nausea or vomiting along with dental pain
- Pus or blood draining from your gums or cheek
What to Do:
- Don’t wait to see your regular dentist—go to the emergency room or an emergency dental clinic if any of these symptoms appear.
- Early intervention with antibiotics, drainage, or surgery can prevent complications and save your life.
Factors Influencing the Timeline
General Health
- Immune System Strength: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as diabetics or chemotherapy patients, are at higher risk of rapid infection spread.
- Existing Conditions: Chronic illnesses can exacerbate the speed at which an infection becomes severe.
Dental Hygiene Practices
- Promptness in Seeking Treatment: Early intervention can halt the progression of the infection.
- Oral Care Routine: Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups can prevent infections from occurring in the first place.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Dental Infections
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
- Brush Twice a Day: Use fluoride toothpaste to help strengthen your teeth.
- Floss Daily: Remove food particles and plaque from between your teeth.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Professional cleanings and exams can catch potential issues before they become serious.
Lifestyle Choices
- Avoid Tobacco Products: Smoking or chewing tobacco can compromise your oral health.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to boost your immune system.
Treatment Options for Dental Infections
Immediate Remedies
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain.
- Saltwater Rinse: Helps to reduce bacteria and ease discomfort
Professional Treatments
- Antibiotics: Necessary to fight the bacterial infection.
- Drainage: The dentist may need to make an incision to drain the abscess.
- Root Canal: Removes the infected pulp.
- Extraction: In severe cases, the affected tooth may need to be removed.
FAQ
How long can you have a dental infection before it becomes serious?
A dental infection can become serious in as little as one week if not treated. Symptoms can quickly escalate, leading to severe health complications.
Can a dental infection go away on its own?
No, a dental infection will not go away on its own. Medical intervention is necessary to treat the infection and prevent it from spreading.
How can you tell if a dental infection is spreading?
Signs of a spreading infection include increased swelling, pain, fever, difficulty breathing or swallowing, and a general feeling of being unwell.
Is a dental infection life-threatening?
Yes, a dental infection can be life-threatening if it spreads to critical areas of the body such as the jaw, sinuses, brain, or bloodstream. Immediate treatment is crucial.
What should I do if I suspect I have a dental infection?
Seek dental care immediately. Early treatment can prevent the infection from becoming severe.
Can I manage a dental infection at home?
No. While over-the-counter pain relievers and saltwater rinses can provide temporary relief, professional dental treatment is necessary to address the root cause of the infection.
Will antibiotics cure a dental infection?
Antibiotics can help manage the infection, but they are often used with other treatments like drainage, root canal, or tooth extraction to fully eradicate the infection.
Dental infections are not just an inconvenience; they are a serious health risk that can escalate rapidly if not treated. Understanding the stages of a dental infection and seeking prompt medical attention can be life-saving. Prioritize your oral hygiene, make regular dental visits, and don’t ignore the early signs of infection. Your health—not just your smile—depends on it.
Take action today to protect yourself from the dangers of dental infections. Schedule a dental check-up, maintain good oral hygiene, and consult a healthcare professional at the first sign of trouble. Your health is your wealth; guard it diligently.