Dental amalgam has been a popular choice for filling cavities for over a century. Amalgam fillings are known for their durability and strength and are composed of a mixture of metals, including mercury, silver, tin, and copper. However, concerns about the safety of amalgam, particularly regarding mercury content, have led many patients to question whether they should opt for this type of filling. In this article, we will explore the benefits and potential dangers of amalgam fillings, helping you make an informed decision about your dental care.
What Are Amalgam Fillings?
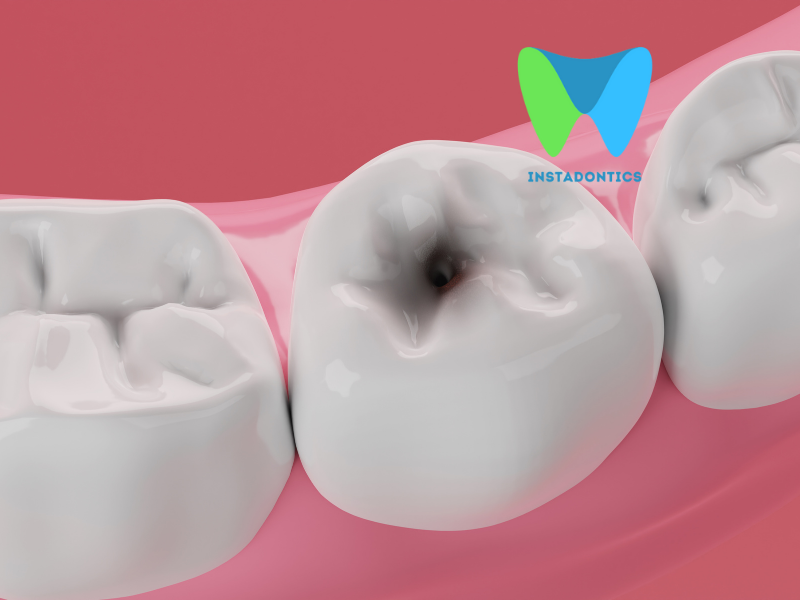
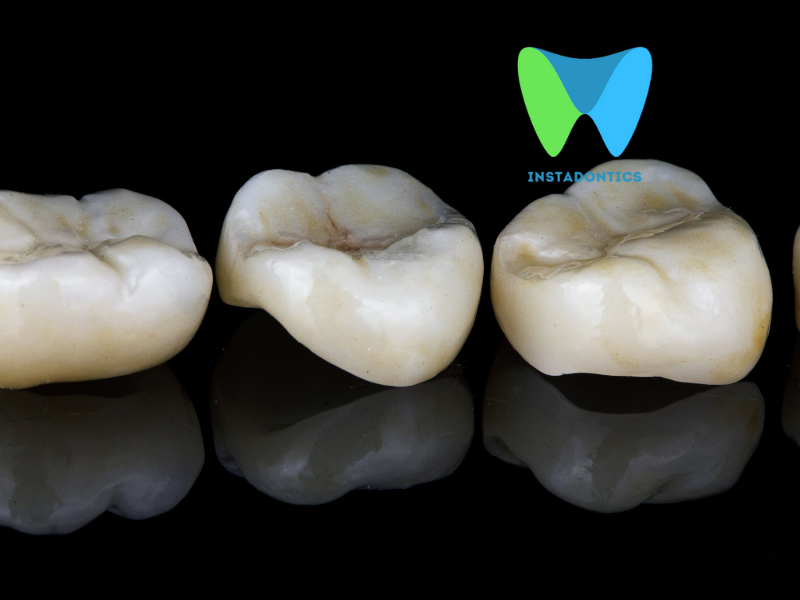
Amalgam fillings are a type of restorative dental material used to fill cavities caused by tooth decay. The primary component of amalgam is elemental mercury, which makes up about 50% of the material. The other metals—silver, tin, and copper—are added to enhance the strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion of the filling. Amalgam is often used for fillings in the back teeth, where chewing pressure is greatest, due to its durability.
Benefits of Amalgam Fillings
- Durability and Longevity: Amalgam fillings are known for their strength and can withstand significant chewing forces, making them suitable for molars and premolars. They typically last 10 to 15 years or longer with proper care.
- Cost-Effective: Amalgam fillings are generally less expensive than composite resin fillings, making them an economical choice for patients.
- Quick Placement: The procedure for placing an amalgam filling is relatively straightforward and can often be completed in one visit. Amalgam does not require curing with a special light, allowing for a faster treatment process.
- Resistance to Wear: Amalgam is less prone to wear and tear compared to some other materials, making it a reliable option for high-stress areas of the mouth.
When to Use Dental Amalgam
Dental amalgam is often chosen for specific situations due to its durability and cost-effectiveness. It is particularly useful in the following scenarios:
- Large Cavities: Amalgam is strong and can withstand the forces of chewing, making it ideal for large cavities, especially in molars.
- Moist Environments: Amalgam is less sensitive to moisture during placement compared to composite resins, making it suitable for areas that are difficult to keep dry.
- Cost-Effective Option: Amalgam is generally less expensive than tooth-coloured alternatives like composite resin or ceramic fillings.
- Longevity: Amalgam fillings are highly durable and can last 10–15 years or longer with proper care.
Potential Dangers and Concerns
Despite the benefits, amalgam fillings have raised concerns, particularly regarding the presence of mercury. Here are some potential dangers associated with amalgam fillings:
- Mercury Exposure:
- Health Concerns: Mercury is a neurotoxin, and exposure to high levels can have harmful effects on health. However, the amount of mercury released from amalgam fillings is considered to be very low and within safety limits established by health organizations. The FDA and the American Dental Association (ADA) state that dental amalgam is safe for most people.
- Vulnerable Populations: Pregnant women, nursing mothers, and individuals with certain health conditions (such as kidney disease) may be advised to avoid amalgam fillings due to potential risks associated with mercury exposure.
- Allergic Reactions:
- Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to the metals in amalgam, particularly mercury or other components. Symptoms can include rashes, itching, or swelling in the mouth. If you have a known allergy to any of the metals used in amalgam, discuss alternative filling options with your dentist.
- Environmental Concerns:
- The disposal of amalgam fillings raises environmental concerns due to mercury contamination. Dental practices are required to follow specific guidelines for the safe disposal of amalgam waste to minimize environmental impact.
- Aesthetic Limitations:
- Amalgam fillings are silver in color and may not blend well with natural tooth enamel, making them less desirable for visible areas of the mouth. Patients seeking a more aesthetic option may prefer composite resin fillings, which can be color-matched to the teeth.
Should You Get an Amalgam Filling?
The decision to get an amalgam filling depends on various factors, including:
- Location of the Cavity: Amalgam is often recommended for back teeth due to its strength and durability. For front teeth or areas that are highly visible, composite fillings may be a better aesthetic choice.
- Personal Health Considerations: If you are pregnant, nursing, or have a health condition that makes you more sensitive to mercury, discuss your options with your dentist. They may recommend alternative materials that do not contain mercury.
- Cost and Longevity: If you are looking for a cost-effective solution that offers durability, amalgam fillings may be suitable for you. Consider your budget and how long you expect the filling to last.
- Dental Professional’s Recommendation: Your dentist will evaluate your specific situation, including the extent of decay and your oral health history, to recommend the most appropriate filling material.
Is Dental Amalgam Safe?
Dental amalgam has been used for over 150 years to fill cavities caused by tooth decay. It is a mixture of metals, consisting of liquid (elemental) mercury and a powdered alloy composed of silver, tin, and copper. Approximately 50% of dental amalgam is elemental mercury by weight. The safety of dental amalgam has been a topic of debate due to concerns about mercury exposure.
Safety Considerations:
- FDA and WHO Stance:
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the World Health Organization (WHO) consider dental amalgam safe for adults and children over the age of 6. The FDA has classified dental amalgam as a Class II medical device, meaning it is considered to have moderate risk.
- The FDA states that the levels of mercury released by amalgam fillings are very low and well below the threshold associated with adverse health effects.
- Mercury Exposure:
- Mercury in amalgam fillings is in a stable form, and the amount released during chewing or brushing is minimal.
- Some studies suggest that mercury vapor can be released during the placement or removal of amalgam fillings, but the levels are generally considered safe for most people.
- High-Risk Groups:
- Pregnant women, nursing mothers, and children under 6 are considered more vulnerable to mercury exposure. The FDA recommends that these groups avoid dental amalgam if possible and opt for alternative materials like composite resin.
- Individuals with kidney disorders or known allergies to mercury or other components of amalgam should also avoid it.
When to Replace Dental Amalgam Fillings
Dental amalgam fillings are long-lasting, but they may need to be replaced under certain circumstances:
- Wear and Tear: Over time, amalgam fillings can wear down, crack, or develop gaps at the edges, allowing bacteria to enter and cause decay.
- Recurrent Decay: If decay develops around or under the filling, it may need to be replaced.
- Cracks or Damage: If the filling or the tooth itself cracks, replacement may be necessary to restore function and prevent further damage.
- Aesthetic Concerns: Some patients choose to replace amalgam fillings with tooth-colored materials for cosmetic reasons.
- Allergic Reactions: Although rare, some individuals may develop an allergic reaction to the metals in amalgam, necessitating replacement.
- Mercury Concerns: Patients who are concerned about mercury exposure may opt to replace amalgam fillings with alternative materials, though this is not medically necessary for most people.
Alternatives to Dental Amalgam
If you prefer not to use dental amalgam, several alternatives are available:
- Composite Resin: Tooth-colored fillings made of a mixture of plastic and glass. They are aesthetically pleasing but may not be as durable as amalgam for large cavities.
- Ceramic (Porcelain) Fillings: These are highly aesthetic and durable but more expensive than composite resin.
- Glass Ionomer: Used for small fillings or in areas with minimal chewing pressure. It releases fluoride, which can help prevent decay.
- Gold Fillings: Extremely durable and biocompatible but expensive and less aesthetically pleasing.
Related: Amalgam Fillings: FAQs & Safety Myths Debunked
Amalgam fillings have been a trusted solution for dental cavities for many years, offering durability and cost-effectiveness. While concerns about mercury exposure and other risks exist, health organizations maintain that amalgam is safe for most individuals. Ultimately, the decision to receive an amalgam filling should be made in consultation with your dentist, considering your unique health needs and preferences. If you have concerns about amalgam or are seeking alternative filling options, don’t hesitate to discuss them with your dental professional to find the best solution for your oral health.