Can Gum Disease Really Cause Tooth Loss? Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a prevalent oral health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. While many may associate gum disease primarily with inflammation and discomfort, its implications extend far beyond these symptoms. One of the most concerning outcomes of untreated gum disease is tooth loss. This in-depth exploration will delve into how gum disease leads to tooth loss, the stages of the disease, risk factors, and preventive measures to maintain oral health.
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease is an infection of the tissues that surround and support the teeth. It is primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth. If plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which can only be removed through professional dental cleanings.
Stages of Gum Disease
Gum disease generally progresses through two main stages:
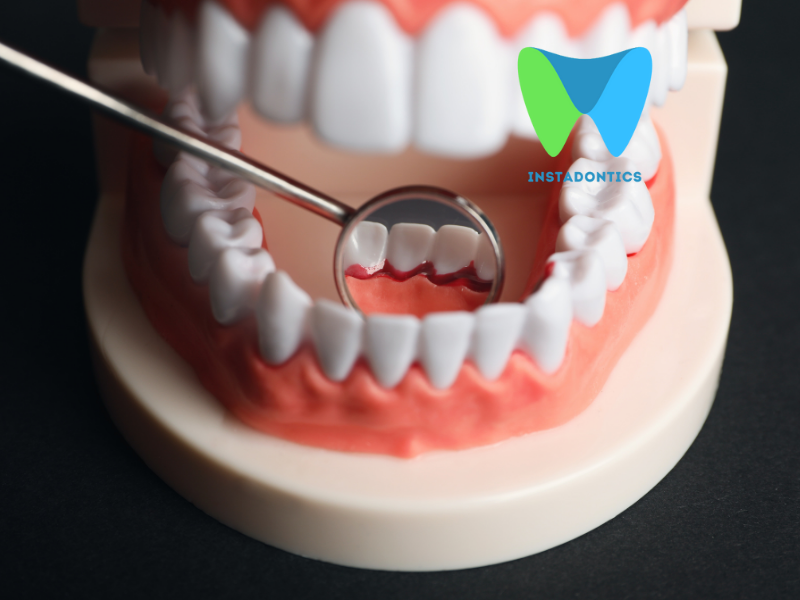
- Gingivitis: This is the earliest stage of gum disease, characterized by inflammation of the gums. Common symptoms include redness, swelling, and bleeding during brushing or flossing. At this stage, the condition is often reversible with good oral hygiene practices and professional dental care.
- Periodontitis: If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis. This stage involves deeper inflammation and infection of the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone. The gums may begin to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that harbor bacteria. As the disease progresses, the supporting bone and tissue can be destroyed, leading to tooth mobility and, ultimately, tooth loss.
How Gum Disease Leads to Tooth Loss
The connection between gum disease and tooth loss is primarily due to the destruction of the supporting structures of the teeth. Here’s a closer look at the mechanisms involved:
1. Destruction of Bone and Tissue
As periodontitis progresses, the body’s immune response to the bacterial infection leads to inflammation. This inflammation can cause the breakdown of the bone and connective tissue that hold the teeth in place. The loss of bone density and tissue integrity compromises the stability of the teeth, making them more susceptible to mobility and eventual loss.
2. Formation of Periodontal Pockets
In periodontitis, the gums begin to recede from the teeth, creating pockets that can trap bacteria and plaque. These pockets can deepen over time, allowing for further bacterial invasion and destruction of the supporting structures. The deeper the pockets, the more challenging it becomes to maintain oral hygiene, leading to a vicious cycle of infection and tissue loss.
3. Tooth Mobility
As the supporting structures deteriorate, teeth may become loose and shift position. This mobility can make it difficult to chew and may cause discomfort. If the condition is not addressed, the affected teeth may eventually fall out or require extraction.
4. Increased Risk of Infection
The presence of gum disease increases the risk of further infections in the oral cavity. Bacteria from periodontal pockets can enter the bloodstream, potentially leading to systemic health issues. This chronic infection can create a cycle of inflammation that exacerbates gum disease and contributes to tooth loss.
Can Gum Disease Cause Tooth Loss?
Risk Factors for Gum Disease and Tooth Loss
Several factors can increase the risk of developing gum disease and, consequently, tooth loss:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to accumulate and harden into tartar, leading to gum disease.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking and other forms of tobacco use significantly impair blood flow to the gums, reducing their ability to heal and increasing the risk of gum disease.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to gum disease, making them more susceptible to its effects.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during pregnancy or menopause, can affect gum sensitivity and health.
- Chronic Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders can increase the risk of gum disease and tooth loss.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: A diet lacking essential nutrients, particularly vitamin C, can hinder the body’s ability to fight infections and maintain healthy gums.
Can Gum Disease Cause Tooth Loss?
Preventive Measures to Maintain Gum Health
Preventing gum disease and its associated risk of tooth loss requires a proactive approach to oral hygiene and overall health. Here are several effective strategies:
1. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
- Brush Twice Daily: Use fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush to brush your teeth for at least two minutes, ensuring you reach all surfaces.
- Floss Daily: Flossing removes plaque and food particles from between the teeth and along the gumline, areas that brushing alone may miss.
- Use Antimicrobial Mouthwash: Incorporating an antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria in the mouth and promote gum health.
2. Regular Dental Check-ups
Routine dental visits are essential for early detection and treatment of gum disease. Dentists can perform professional cleanings to remove tartar and monitor gum health. Regular check-ups also provide an opportunity to discuss any concerns and receive personalized advice.
3. Quit Smoking
If you smoke, quitting can significantly improve your gum health and reduce the risk of tooth loss. Seek support from healthcare professionals or cessation programs to help you quit.
4. Eat a Balanced Diet
A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C and calcium, supports healthy gums. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your diet.
5. Manage Chronic Conditions
If you have chronic health conditions such as diabetes, work with your healthcare provider to manage them effectively. Controlling these conditions can help reduce the risk of developing gum disease.
6. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps maintain saliva production, which is essential for neutralizing acids and washing away food particles and bacteria.
15 FAQs About Gum Disease and Tooth Loss
1. What are the early signs of gum disease?
Red, swollen, bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing.
2. Is gum disease reversible?
Gingivitis, the early stage, is reversible with professional cleaning and good oral hygiene.
3. How does gum disease lead to tooth loss?
By damaging the bone and tissue that support your teeth.
4. Can you have gum disease without knowing it?
Yes, especially in early stages — it can be painless and subtle.
5. What causes gum disease?
Mostly poor oral hygiene, but smoking, diabetes, genetics, and stress can contribute too.
6. Who is most at risk for gum disease?
Smokers, diabetics, older adults, and those with a family history of gum disease.
7. How is gum disease diagnosed?
A dentist checks for gum bleeding, pocket depth, loose teeth, and bone loss through exams and X-rays.
8. What treatments are available for gum disease?
Scaling and root planing (deep cleaning), antibiotics, and sometimes surgery for severe cases.
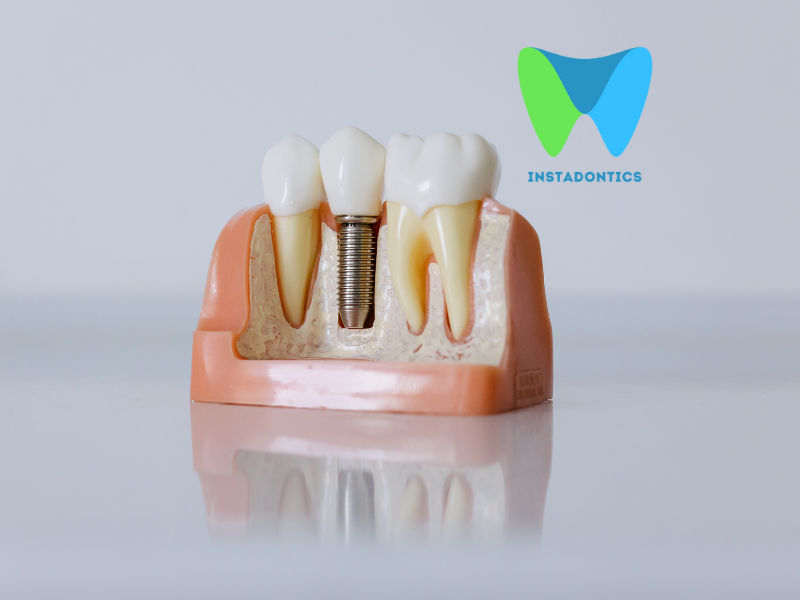
9. Can lost teeth from gum disease be replaced?
Yes, with dental implants, bridges, or dentures — but healthy gums are needed first.
10. Does brushing and flossing really prevent gum disease?
Absolutely — daily brushing, flossing, and regular dental visits are key preventatives.
11. Can children get gum disease?
Yes, though it’s less common; they can develop a milder form called gingivitis.
12. Does gum disease affect overall health?
Yes, it’s linked to heart disease, diabetes complications, and even pregnancy issues.
13. Can you stop gum disease once it has started?
You can manage it and prevent further damage with professional help and diligent home care.
14. How fast does gum disease progress?
It varies — some people develop severe disease quickly, others slowly over years.
15.Can Gum Disease Really Cause Tooth Loss?
Yes, gum disease (also known as periodontal disease) is a major cause of tooth loss, especially in adults. The good news? With early detection and proper treatment, gum disease can often be managed or even reversed before it causes permanent damage.
15. What happens if gum disease is left untreated?
It can lead to gum recession, bone loss, loose teeth, and ultimately, tooth loss.
Gum disease is a serious condition that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. The connection between gum health and overall oral health cannot be overstated, and understanding the mechanisms of gum disease is crucial for prevention and treatment. By maintaining good oral hygiene, seeking regular dental care, and addressing risk factors, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of gum disease and preserve their natural teeth.
If you suspect you have gum disease or are experiencing symptoms such as swollen or bleeding gums, it is essential to consult a dental professional promptly. Early intervention can make a significant difference in managing gum disease and preventing tooth loss, ensuring a healthier smile for years to come.