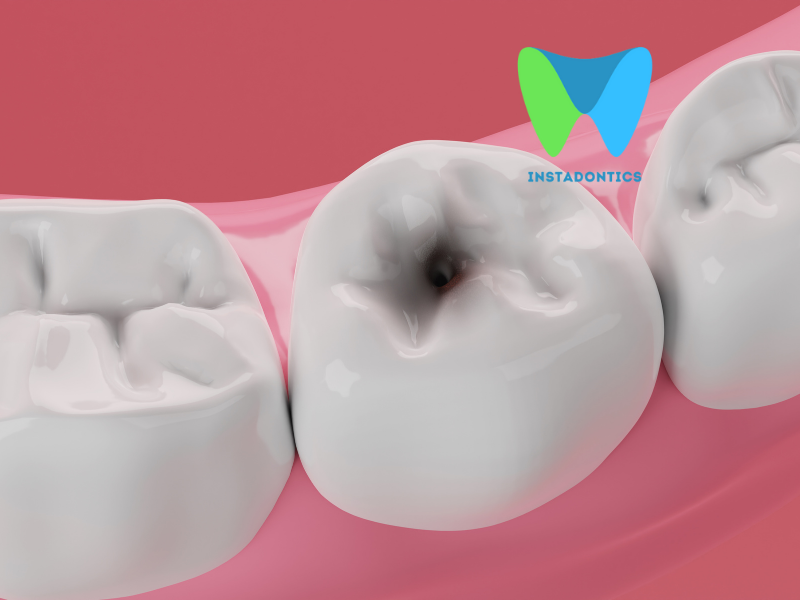
A dental abscess is a painful and potentially serious condition that occurs when a pocket of pus forms in the teeth or gums due to a bacterial infection. It’s not just a minor dental issue—it’s a warning sign that something is seriously wrong and requires immediate attention. Left untreated, a dental abscess can lead to severe complications, including the spread of infection to other parts of the body. In this in-depth blog, we’ll explore what a dental abscess is, its causes, symptoms, and why you should never ignore it. We’ll also discuss treatment options and how to prevent this painful condition from occurring in the first place.
What Is a Dental Abscess?
A dental abscess is a localized collection of pus that forms in response to a bacterial infection. It can occur in different parts of the tooth or gums, depending on the underlying cause. There are three main types of dental abscesses:
- Periapical Abscess: This type of abscess occurs at the tip of the tooth’s root. It is usually caused by an untreated cavity, trauma, or a cracked tooth that allows bacteria to infect the pulp (the innermost part of the tooth containing nerves and blood vessels).
- Periodontal Abscess: This abscess forms in the gums next to a tooth root, often as a result of advanced gum disease (periodontitis). It can also occur due to food particles becoming trapped in the gum pockets.
- Gingival Abscess: This type of abscess is confined to the gum tissue and does not affect the tooth or periodontal ligament. It is often caused by injury or foreign objects, such as a popcorn kernel or toothpick, becoming lodged in the gums.
Regardless of the type, a dental abscess is a serious condition that requires prompt treatment to prevent the infection from spreading and causing further damage.
Related: Fistula vs. Abscess in Dentistry: Key Differences
What Causes an Abscess?
A dental abscess is caused by a bacterial infection, but several factors can increase your risk of developing one. These include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Failing to brush and floss regularly allows plaque to build up on your teeth, leading to cavities and gum disease—both of which can result in an abscess.
- Untreated Cavities: When cavities are left untreated, bacteria can penetrate the tooth’s enamel and dentin, eventually reaching the pulp and causing an infection.
- Gum Disease: Advanced gum disease can cause the gums to pull away from the teeth, creating pockets where bacteria can thrive and form an abscess.
- Trauma to the Tooth: A cracked, chipped, or broken tooth can provide an entry point for bacteria, leading to an infection.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions such as diabetes, autoimmune diseases, or treatments like chemotherapy can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections.
- Dry Mouth: Saliva helps wash away bacteria and food particles. A dry mouth, often caused by medications or medical conditions, can increase the risk of tooth decay and abscesses.
- Diet High in Sugar: Consuming excessive amounts of sugar feeds the bacteria in your mouth, increasing the likelihood of cavities and infections.
Symptoms
A dental abscess is often accompanied by a range of symptoms, some of which can be severe. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for seeking timely treatment. Common signs of a dental abscess include:
- Severe, Throbbing Toothache: One of the most common symptoms of a dental abscess is intense, persistent pain that may radiate to the jaw, ear, or neck. The pain often worsens when lying down or applying pressure to the affected tooth.
- Swelling in the Face, Cheek, or Gums: Swelling is a clear sign of infection. In some cases, the swelling can be significant, causing visible asymmetry in the face.
- Sensitivity to Hot and Cold: The affected tooth may become extremely sensitive to hot or cold temperatures, even after the stimulus is removed.
- Fever: A fever is your body’s response to fighting an infection. If you have a dental abscess, you may experience a fever along with other flu-like symptoms, such as fatigue and chills.
- Bad Breath or a Foul Taste in the Mouth: The pus from the abscess can cause a persistent bad taste or odor in your mouth, even after brushing or rinsing.
- Difficulty Opening Your Mouth or Swallowing: Swelling and pain can make it difficult to open your mouth fully or swallow, which is a sign that the infection may be spreading.
- Tender, Swollen Lymph Nodes: The lymph nodes under your jaw or in your neck may become swollen and tender as your body tries to fight the infection.
- A Visible Pimple on the Gums: A small, pimple-like bump on the gums, known as a “gum boil” or “draining fistula,” is a classic sign of a dental abscess. It may ooze pus, providing temporary relief from pain.
- Loose or Discolored Tooth: The affected tooth may become loose or discolored due to the infection damaging the surrounding tissues.
- General Malaise: Feeling unwell, fatigued, or generally run-down can be a sign that your body is fighting an infection.
Why You Should Never Ignore a Dental Abscess
Ignoring a dental abscess can have serious consequences for your oral and overall health. Here’s why you should never delay seeking treatment:
- Spread of Infection: The infection from a dental abscess can spread to other parts of your body, including your jaw, neck, sinuses, and even your brain. In rare cases, it can lead to life-threatening conditions such as sepsis or Ludwig’s angina (a severe infection of the floor of the mouth).
- Tooth Loss: An untreated abscess can destroy the bone and tissues supporting the affected tooth, leading to tooth loss.
- Chronic Pain: The pain from a dental abscess can become chronic and debilitating, affecting your ability to eat, speak, and sleep.
- Increased Treatment Complexity: What might have been a simple dental procedure, such as a filling or root canal, can become more complex and costly if the infection is allowed to progress.
- Impact on Overall Health: Dental infections have been linked to systemic health issues, including heart disease, diabetes complications, and respiratory infections.
How Is a Dental Abscess Treated?
The treatment for a dental abscess depends on the severity and location of the infection. Common treatment options include:
- Drainage of the Abscess: The dentist will make a small incision to drain the pus, providing immediate relief from pain and pressure.
- Root Canal Therapy: If the abscess is caused by an infected tooth pulp, a root canal may be performed to remove the infected tissue and save the tooth.
- Tooth Extraction: In cases where the tooth cannot be saved, extraction may be necessary to prevent the infection from spreading.
- Antibiotics: If the infection has spread or if you have a weakened immune system, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help clear the infection.
- Scaling and Root Planing: For periodontal abscesses, a deep cleaning procedure may be performed to remove plaque and bacteria from below the gumline.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Image of Dental Abscess
How to Prevent a Dental Abscess
Preventing a dental abscess starts with good oral hygiene and regular dental care. Here are some tips to reduce your risk:
- Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth.
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
- Limit sugary foods and drinks, which can contribute to tooth decay.
- Wear a mouthguard if you grind your teeth at night.
- Address dental issues, such as cavities or gum disease, as soon as they arise.
A dental abscess is a serious condition that requires immediate attention. Ignoring the symptoms can lead to severe complications, including the spread of infection, tooth loss, and even life-threatening conditions. By recognizing the signs of a dental abscess and seeking prompt treatment, you can protect your oral and overall health. Remember, prevention is always better than cure—maintaining good oral hygiene and visiting your dentist regularly are the best ways to avoid this painful and potentially dangerous condition. If you suspect you have a dental abscess, don’t wait. Contact your dentist right away and take the first step toward recovery. Your health and well-being depend on it.