Understanding Dental Abscesses: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
A dental abscess is a painful oral condition that can escalate quickly if not treated. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down what a dental abscess is, its causes, symptoms, and how it can be treated effectively. Whether you’re experiencing symptoms or just want to be informed, this article provides valuable insights into this common dental issue.
What is a Dental Abscess?
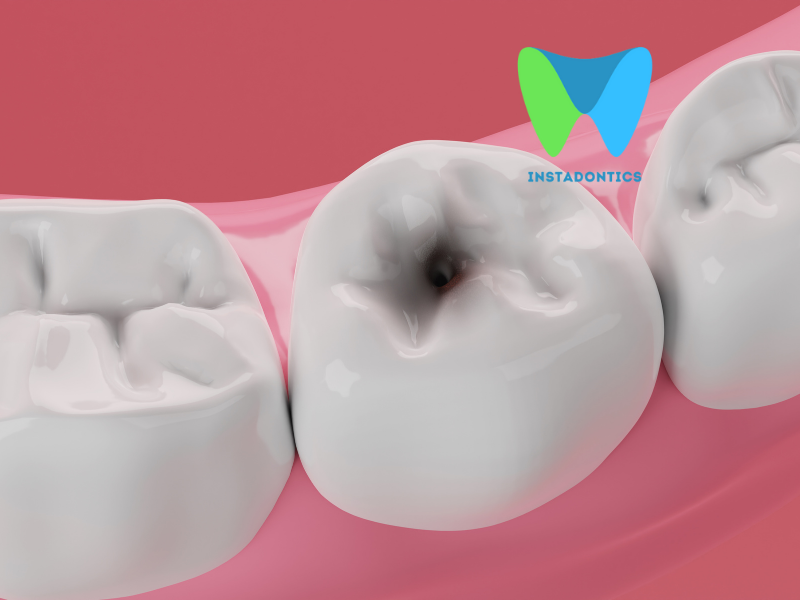
A dental abscess is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection in or around a tooth. It typically forms when bacteria enter the tooth through decay, chips, or cracks and spread to the root or surrounding gum tissue.
There are three main types of dental abscesses:
- Periapical Abscess: Forms at the tip of the tooth root.
- Periodontal Abscess: Develops in the gums near the root of the tooth.
- Gingival Abscess: Occurs in the gum tissue without affecting the tooth or bone.
Dental abscesses are a sign of severe infection and should not be ignored.
Dental Definition of an Abscess
A dental abscess is a localized collection of pus within the teeth, gums, or surrounding bone structures, caused by a bacterial infection. It occurs when bacteria invade the dental pulp (the inner, living part of the tooth) or the supporting gum tissue, leading to inflammation and the accumulation of pus.
Types of Dental Abscesses
- Periapical Abscess:
- Location: Forms at the tip of the tooth’s root.
- Cause: Often results from untreated tooth decay, where bacteria penetrate through the enamel and dentin, reaching the pulp and infecting the root canal.
- Symptoms: Severe toothache, swelling, and sensitivity to pressure or temperature.
- Periodontal Abscess:
- Location: Occurs in the supporting gum tissue surrounding a tooth.
- Cause: Frequently linked to advanced gum disease (periodontitis), which creates pockets where bacteria thrive, leading to infection.
- Symptoms: Swollen, red gums that may bleed, along with discomfort when chewing.
- Gingival Abscess:
- Location: Found in the gum tissue, not affecting the tooth or its root.
- Cause: Often triggered by foreign objects, such as food particles or debris, becoming trapped in the gums.
- Symptoms: Localized swelling and tenderness in the gums.
Key Characteristics of a Dental Abscess
- Pus Formation: Pus consists of dead white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris, which accumulate due to the immune system’s response to infection.
- Inflammation: Surrounding tissues become red, swollen, and painful as the body fights off the infection.
- Fistula Development: In some cases, the abscess may form a small channel (fistula) through the gum or skin, allowing pus to drain and providing temporary relief.
Dental Abscesses: Pathophysiology
- Initial Infection:
- Begins when bacteria infiltrate through dental caries, gum pockets, or a cracked tooth.
- Immune Response:
- The body sends white blood cells to fight the infection, leading to localized inflammation.
- Pus Accumulation:
- As the infection progresses, the immune response causes pus to collect in the area, forming an abscess.
- Pressure Build-Up:
- The abscess grows, causing significant pressure and pain. If untreated, it may spread to nearby tissues or the bloodstream, resulting in severe complications.
Diagnosis of a Dental Abscess
Dentists diagnose an abscess using:
- Clinical Examination: Checking for visible swelling, redness, or pus drainage.
- X-rays: Identifying the location and extent of the abscess, including bone damage or infection spread.
- Pulp Vitality Tests: Assessing whether the tooth’s pulp is alive or necrotic (dead).
What Causes a Dental Abscess?
Several factors can lead to the development of a dental abscess:
- Tooth Decay: Untreated cavities can expose the tooth’s inner pulp to bacteria.
- Gum Disease: Periodontitis creates pockets where bacteria thrive.
- Dental Trauma: Chipped or cracked teeth can allow bacteria to penetrate deep into the tooth.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Neglecting brushing, flossing, and dental checkups increases infection risk.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions like diabetes can make infections more likely.
Common Symptoms of a Dental Abscess
Dental abscesses can be extremely painful and present a range of symptoms, including:
- Severe, throbbing toothache that may radiate to the jaw, neck, or ear.
- Swelling in the face or cheek.
- Red, swollen gums around the affected area.
- Sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks.
- Bad breath or a foul taste in the mouth.
- Fever and general feeling of illness.
- Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or opening the mouth fully.
If you notice these symptoms, seek immediate dental care to prevent complications.
Complications of Untreated Dental Abscesses
An untreated dental abscess can lead to serious complications, such as:
- Spread of Infection: Bacteria can enter the bloodstream, causing a life-threatening condition called sepsis.
- Bone Loss: Prolonged infection may erode the surrounding bone.
- Tooth Loss: Advanced infection may necessitate tooth extraction.
Prompt treatment can prevent these outcomes.
How is a Dental Abscess Treated?
Treatment focuses on eliminating the infection and relieving pain. Common procedures include:
- Drainage of the Abscess: The dentist makes a small incision to drain pus and reduce swelling.
- Root Canal Therapy: Removes infected pulp and seals the tooth to prevent reinfection.
- Tooth Extraction: In severe cases, the tooth may need to be removed to stop the infection.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed to control and eliminate bacterial infections.
Preventing Dental Abscesses
Preventive care is key to avoiding dental abscesses. Follow these tips:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles.
- Visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups.
- Treat cavities and gum disease promptly.
- Avoid excessive consumption of sugary foods and beverages.
When to See a Dentist
If you experience persistent tooth pain, swelling, or any of the symptoms mentioned, schedule an appointment with your dentist immediately. Dental abscesses require professional care to prevent complications and restore oral health.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dental Abscesses
1. What is the main cause of a dental abscess?
The primary cause of a dental abscess is a bacterial infection. This often occurs when bacteria enter the tooth through untreated cavities, cracks, or gum disease. Poor oral hygiene and dental trauma can also contribute.
2. How do I know if I have a dental abscess?
Common signs of a dental abscess include:
- Severe, throbbing toothache.
- Swollen gums or face.
- A foul taste in your mouth or bad breath.
- Fever or general malaise.
If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a dentist immediately.
3. Can a dental abscess go away on its own?
No, a dental abscess will not heal on its own. The infection can spread to other areas of the body, leading to severe complications. It is essential to seek professional dental care to treat the abscess.
4. Is a dental abscess an emergency?
Yes, a dental abscess is considered a dental emergency. If left untreated, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, causing serious health issues. Visit a dentist as soon as possible if you suspect you have an abscess.
5. What should I do while waiting to see a dentist?
While waiting for a dental appointment, you can:
- Rinse your mouth with warm saltwater to reduce swelling.
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen to manage discomfort.
- Avoid chewing on the affected side.
- Do not attempt to drain the abscess yourself, as this can worsen the infection.
6. Can antibiotics alone cure a dental abscess?
Antibiotics can help control the infection and reduce symptoms, but they won’t eliminate the source of the abscess. Dental procedures like drainage, a root canal, or extraction are usually required for complete treatment.
7. How long does it take to recover from a dental abscess?
Recovery depends on the severity of the abscess and the type of treatment. Most people feel relief within a few days after treatment, but it may take a week or two for complete healing.
8. How can I prevent a dental abscess in the future?
To prevent dental abscesses:
- Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing daily.
- Visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups.
- Address cavities and gum issues promptly.
- Avoid excessive sugary foods and drinks.
9. Can children get dental abscesses?
Yes, children can develop dental abscesses, often due to untreated cavities, poor oral hygiene, or trauma to their teeth. Ensure your child practices good dental care and sees a dentist regularly.
10. Are dental abscesses contagious?
No, a dental abscess itself is not contagious. However, the bacteria causing the abscess can spread through saliva. Practicing good oral hygiene and avoiding sharing utensils can reduce the risk of bacterial transfer.
If you have more questions or concerns about dental abscesses, consult with a dental professional for personalized advice!
A dental abscess is more than just a painful inconvenience—it’s a serious condition that requires prompt attention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to protect your oral health. Regular dental care and good hygiene practices are your best defenses against dental abscesses and other oral health issues.