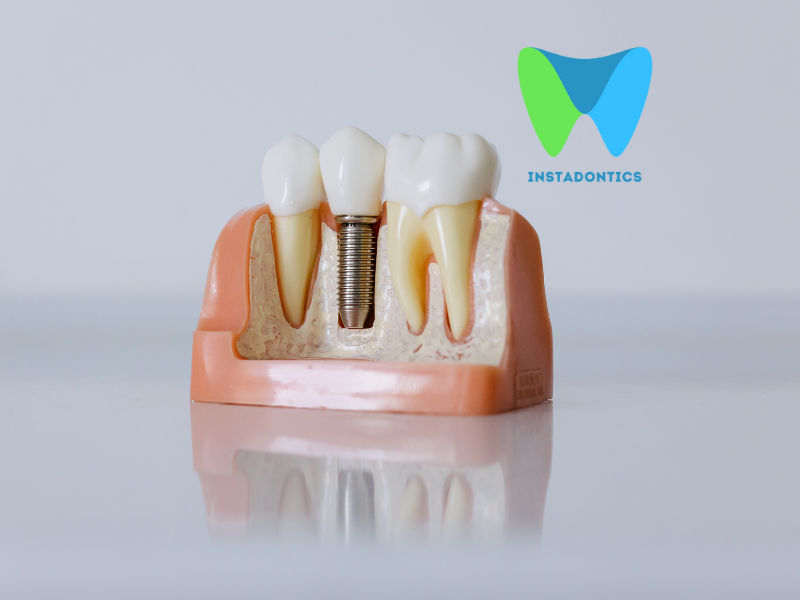
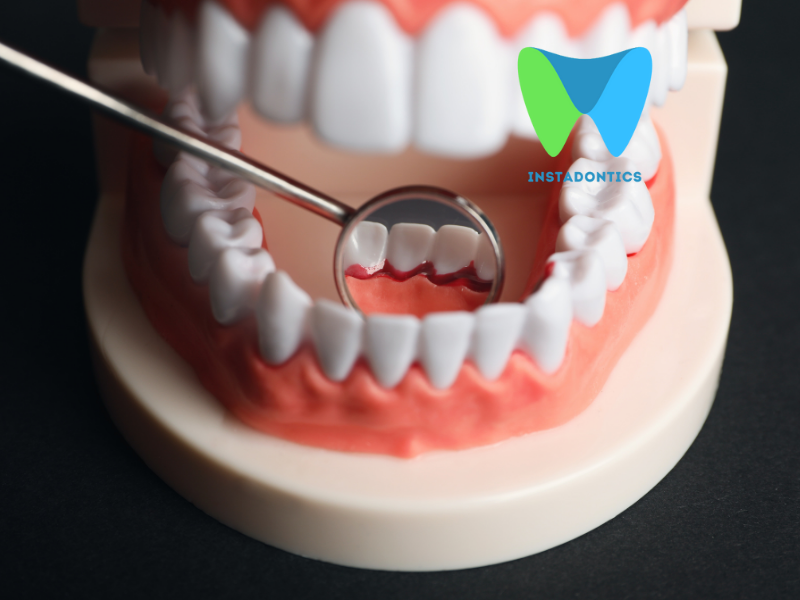
Understanding Gum Disease and Its Prevention
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues that hold your teeth in place. It typically arises from poor oral hygiene, which allows plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to build up on the teeth and harden. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to serious oral health problems. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and preventive measures is essential for maintaining healthy gums and a beautiful smile.
Types of Gum Disease
- Gingivitis: This is the mildest form of gum disease, characterized by redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums.
- Periodontitis: A more severe form of gum disease, periodontitis can cause damage to the soft tissue and bone that support the teeth.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
Common symptoms include:
- Bleeding gums during and after brushing
- Persistent bad breath
- Red, swollen gums
- Receding gums
- Formation of deep pockets between teeth and gums
- Loose or shifting teeth
Causes of Gum Disease
Several factors contribute to the development of gum disease:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to form and harden, leading to gum inflammation.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Tobacco significantly increases the risk of gum disease by reducing blood flow to the gums and making them more susceptible to infection.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to gum disease, regardless of their oral hygiene practices.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes and hormonal changes can elevate the risk of developing gum disease.
How to Prevent Gum Disease
Preventing gum disease is achievable through proper oral hygiene, healthy lifestyle choices, and regular dental care. Here’s a detailed guide on effective prevention strategies:
- Maintain Excellent Oral Hygiene
- Brush Twice Daily: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, brushing for at least two minutes each time.
- Floss Daily: Flossing removes plaque and food particles from between teeth and under the gumline.
- Use Mouthwash: An antimicrobial or fluoride mouthwash can help reduce bacteria and strengthen teeth.
- Clean Your Tongue: Use a tongue scraper or your toothbrush to eliminate bacteria from your tongue.
- Visit Your Dentist Regularly
- Professional Cleanings: Aim for dental cleanings every six months to remove tartar that regular brushing can’t.
- Early Detection: Your dentist can identify early signs of gum disease and provide necessary treatment before it progresses.
- Personalized Advice: Dentists can recommend specific products or techniques tailored to your oral health needs.
- Quit Smoking and Tobacco Use
- Why Quit: Tobacco weakens the immune system and makes it harder for gums to heal.
- How to Quit: Seek support from cessation programs, nicotine replacement therapies, or counseling.
- Eat a Balanced Diet
- Foods to Include: Focus on fruits and vegetables, calcium-rich foods, and vitamin C-rich foods to promote gum health.
- Foods to Avoid: Limit sugary and starchy foods that feed harmful bacteria and acidic foods that can irritate gums.
- Manage Stress
- Stress-Reduction Techniques: Engage in regular exercise, mindfulness, meditation, or yoga. Address teeth grinding with a mouthguard if necessary.
- Stay Hydrated
- Drink Water: Maintain hydration to support healthy saliva production.
- Chew Sugar-Free Gum: This can stimulate saliva flow, especially after meals.
- Avoid Harmful Habits
- Don’t Use Your Teeth as Tools: Avoid using your teeth to open packages or crack nuts.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol can dry out the mouth and increase bacteria growth.
- Monitor and Manage Health Conditions
- Diabetes: Work with your doctor to manage diabetes effectively.
- Hormonal Changes: Maintain good oral hygiene during periods of hormonal fluctuation.
- Medications: Inform your dentist about any medications that may affect gum health.
- Use the Right Tools
- Toothbrush: Choose a soft-bristled brush and replace it every 3-4 months.
- Floss: Use traditional floss, floss picks, or water flossers.
- Mouthwash: Opt for an antimicrobial or fluoride mouthwash.
- Recognize Early Signs of Gum Disease
- Symptoms to Watch For: Red, swollen, or tender gums, bleeding during brushing or flossing, persistent bad breath, receding gums, and loose teeth. If you notice any of these symptoms, consult your dentist immediately.
- Consider Professional Treatments
- If you’re at high risk for gum disease, your dentist may recommend additional preventive measures such as scaling and root planing, antibacterial treatments, or dental sealants.
Risk Factors for Gum Disease
Understanding the risk factors for gum disease can aid in prevention and early intervention. Key risk factors include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate care allows plaque to build up.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Significantly increases risk.
- Genetics: Family history may predispose individuals.
- Hormonal Changes: Can increase gum sensitivity.
- Diabetes: Weakens the immune response.
- Medications: Some can affect saliva flow or cause gum overgrowth.
- Poor Nutrition: A diet lacking essential nutrients can weaken immunity.
- Stress: Can lead to bruxism and weaken the immune system.
- Age: Older adults are at higher risk.
- Crooked Teeth or Poorly Fitted Dental Appliances: Can trap bacteria and irritate gums.
- Chronic Illnesses: Conditions like HIV/AIDS or cancer can compromise immunity.
- Teeth Grinding (Bruxism): Puts pressure on gums and teeth.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
Treatment for gum disease varies depending on severity. Effective options include:
- Professional Dental Cleaning: Essential for removing plaque and tartar.
- Scaling and Root Planing: A deep-cleaning procedure that smooths tooth roots to promote gum reattachment.
- Medications: Antimicrobial and antibiotic treatments can reduce bacteria beneath the gums.
- Surgery: In advanced cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to restore supportive tissues.
Importance of Oral Hygiene
Maintaining proper oral hygiene is crucial for preventing gum disease. Here are some key practices:
- Proper Brushing Techniques: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, brushing for at least two minutes.
- Flossing: Essential for removing plaque from areas a toothbrush can’t reach.
- Choosing the Right Products: Look for ADA-approved toothpaste and gentle toothbrushes.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Gum Disease
- Quitting Smoking: Improves oral health and reduces disease risk.
- Reducing Stress: Techniques like meditation can boost immunity.
- Managing Medical Conditions: Control diabetes and other health issues that affect gum health.
Home Remedies for Gum Disease
In addition to professional treatments and preventive measures, some home remedies may help alleviate symptoms of gum disease and promote oral health:
- Saltwater Rinse: Rinsing with a mixture of salt and warm water can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria. This simple solution can provide temporary relief and promote healing.
- Hydrogen Peroxide Rinse: A mild antiseptic, hydrogen peroxide can help alleviate symptoms of gum disease. Mix equal parts of hydrogen peroxide and water, swish it around your mouth, and then rinse with water afterward.
- Turmeric Paste: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, turmeric can be used to create a paste. Mix turmeric powder with a little water to form a paste, apply it to the gums, and let it sit for a few minutes before rinsing.
Impact of Diet on Gum Health
Your diet plays a significant role in maintaining gum health. Here are some dietary considerations:
- Foods that Promote Gum Health:
- Vitamin C-Rich Foods: Citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers are excellent sources of vitamin C, which is vital for gum health and healing.
- Calcium-Rich Foods: Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods help strengthen teeth and bones.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish like salmon and walnuts, these can help reduce inflammation in the gums.
- Foods to Avoid:
- Sugary Foods and Drinks: High sugar intake can lead to plaque buildup and increase the risk of gum disease.
- Acidic Foods: These can erode enamel and irritate gums, making them more susceptible to disease.
Role of Hydration in Gum Health
Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining healthy gums:
- Importance of Drinking Water: Water helps wash away food particles and bacteria, reducing the risk of gum disease. It also supports saliva production, which is crucial for oral health.
- Effects of Dehydration on Gums: Dehydration can lead to reduced saliva flow, increasing the likelihood of plaque buildup and gum irritation.
Natural Supplements for Gum Health
In addition to a balanced diet, certain vitamins and minerals can support gum health:
- Vitamins and Minerals:
- Vitamin C: Promotes healthy gums and connective tissue, aiding in the healing process.
- Vitamin D: Supports bone health and immune function, which is vital for combating infections.
- Calcium: Essential for strong teeth and bones, helping to maintain overall oral health.
- Herbal Supplements:
- Coenzyme Q10: This antioxidant may help repair gum tissue and reduce inflammation.
- Aloe Vera: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, aloe vera can soothe irritated gums and promote healing.
FAQ about Gum Disease
How to prevent gum disease?
Preventing gum disease requires a combination of good oral hygiene practices, a healthy diet, regular dental check-ups, and lifestyle changes. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, you can maintain healthy gums and avoid the complications associated with gum disease.
What are Early Signs of Gum Disease?
Early detection of gum disease is critical for effective treatment and can prevent its progression to more serious stages. Here are some early signs of gum disease:
- Red and Swollen Gums: Healthy gums are firm and pink. If your gums are red, swollen, and tender, it’s an early sign of gum disease.
- Bleeding Gums: Gums that bleed easily during and after brushing are common early symptoms.
- Persistent Bad Breath: Also known as halitosis, persistent bad breath that doesn’t go away after brushing may indicate gum disease.
- Receding Gums: If your teeth appear longer than normal, it could be a sign your gums are receding, a symptom of gum disease.
Can Gum Disease be Reversed?
Yes, the early stages of gum disease, specifically gingivitis, can often be reversed with diligent oral hygiene and professional dental care. This includes regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings. However, more advanced stages, such as periodontitis, require more intensive treatment and may not be completely reversible.
Preventing and managing gum disease is essential for maintaining overall oral health. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and risk factors associated with gum disease, you can take proactive steps to protect your gums. Regular dental visits, a consistent oral hygiene routine, a balanced diet, and healthy lifestyle choices are your best defenses against gum disease. If you notice any signs of gum disease, seek professional care immediately to prevent further damage and ensure a healthy smile for years to come. Remember, your oral health is an integral part of your overall well-being, so prioritize it in your daily routine.