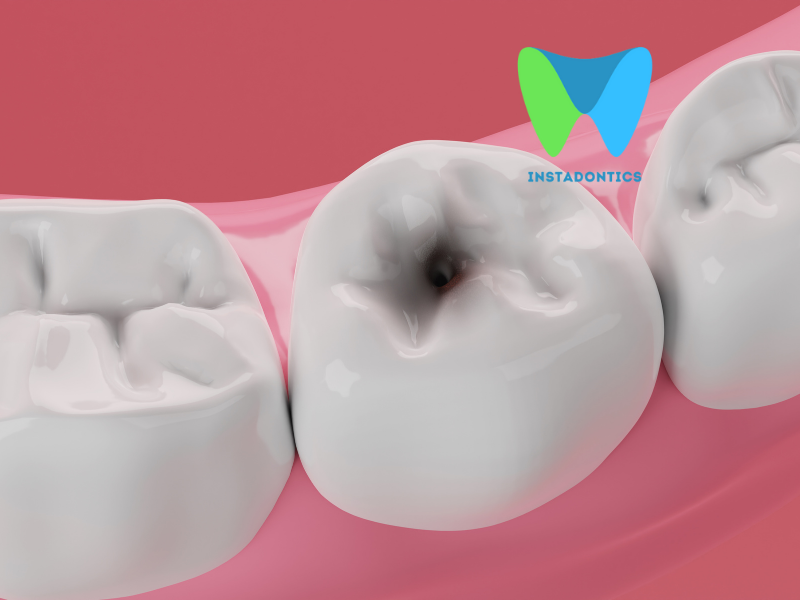
A dental abscess is a collection of pus that forms in or around a tooth or the gums due to a bacterial infection. If not treated promptly, this condition can cause significant pain, swelling, and other complications.
Understanding dental abscesses is crucial because they can lead to severe health issues if neglected. Recognizing the symptoms and knowing when to seek treatment can prevent complications and improve oral health.
Types and Categories
Periapical Abscess
A periapical abscess occurs at the tip of the root of a tooth. It typically results from an untreated dental cavity, injury, or previous dental work that allows bacteria to enter the tooth pulp.
Periodontal Abscess
A periodontal abscess affects the gums and the supporting bone structure of the teeth. It is often caused by gum disease or injury to the gums.
Gingival Abscess
A gingival abscess occurs in the gum tissue, usually without affecting the tooth or the periodontal ligament. It is typically caused by foreign objects, such as food particles, becoming trapped in the gums.
Symptoms and Signs
Common Symptoms
- Severe, persistent, and throbbing toothache
- Sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures
- Swelling in the face, cheek, or neck
- Tender, swollen lymph nodes under the jaw or in the neck
Severe Symptoms
Symptoms can escalate to fever, difficulty breathing or swallowing, and an unpleasant taste in the mouth due to pus drainage. Such indications signal that the infection could spread and necessitate urgent medical care.
- Fever
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Foul taste in the mouth
- Pus drainage from the abscess
Uncommon Symptoms
- Bad breath
- Swollen jaw
- Difficulty opening the mouth
Causes and Risk Factors
Bacterial Infection
Dental abscesses are primarily caused by bacterial infections. These bacteria can invade the dental pulp through cavities, cracks, or chips in the teeth.
Poor Dental Hygiene
Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, which harbors bacteria and increases the risk of infections and abscess formation.
Underlying Health Conditions
Certain health conditions, such as diabetes and autoimmune diseases, can predispose individuals to dental abscesses due to weakened immune responses.
Risk Factors
- High sugar diet
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Dry mouth conditions
Diagnosis and Tests
Visual Examination
A dentist can often diagnose a dental abscess through a visual examination of the affected area.
Dental X-rays
X-rays help identify the extent of the infection and the presence of any underlying issues, such as bone loss or cavities.
Percussion Testing
This involves tapping on the affected tooth to determine if there is pain, which can indicate the presence of an abscess.
Other Diagnostic Tools
- Thermal tests
- Pulp vitality tests
- Blood tests in severe cases
Treatment Options
Timely intervention is essential to prevent the spread of infection and avoid severe complications. Regular dental check-ups facilitate early detection and treatment of potential issues, helping maintain oral hygiene and health.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are a common treatment for dental abscesses, which are caused by bacterial infections. When an abscess forms, bacteria invade the tooth’s pulp or surrounding tissues, leading to pain, swelling, and sometimes systemic symptoms like fever. Antibiotics such as amoxicillin, clindamycin, or metronidazole are often prescribed to eliminate the infection and prevent it from spreading to other parts of the body. However, antibiotics alone are not a definitive solution; they are typically used in conjunction with other treatments like drainage or a root canal to fully address the issue. It’s important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed to ensure the infection is completely eradicated.
Drainage Procedures
In cases where a dental abscess has formed a pocket of pus, drainage is often necessary to relieve pressure and remove the infection. A dentist or oral surgeon may perform a minor procedure to drain the abscess by making a small incision in the gum tissue. This allows the pus to escape, reducing swelling and pain. Local anesthesia is typically used to numb the area, making the procedure relatively comfortable for the patient. After drainage, the area is cleaned, and the patient may be prescribed antibiotics to prevent further infection. Drainage provides immediate relief and is often the first step in treating a severe abscess.
Root Canal Treatment
A root canal is a common and effective treatment for saving a tooth that has been severely infected or abscessed. During this procedure, the dentist removes the infected or inflamed pulp from inside the tooth, cleans and disinfects the root canals, and then fills and seals them to prevent reinfection. Afterward, a crown is usually placed over the tooth to restore its strength and function. Root canal treatment not only eliminates the source of the infection but also preserves the natural tooth, avoiding the need for extraction. Modern techniques and anesthesia make the procedure relatively painless, and it is often the preferred option for treating abscessed teeth.
Tooth Extraction
In severe cases where the tooth is too damaged to be saved, or if the infection poses a significant risk to surrounding tissues, extraction may be necessary. Tooth extraction involves removing the affected tooth entirely to eliminate the source of the infection. While this is typically a last resort, it may be the best option for preventing the spread of infection to other teeth or areas of the body. After extraction, the dentist may discuss replacement options, such as dental implants, bridges, or dentures, to restore function and aesthetics. Proper aftercare, including antibiotics and pain management, is essential to ensure proper healing.
Pain Management
Dental abscesses can cause significant pain and discomfort, making pain management an important part of treatment. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen are often recommended to reduce pain and inflammation. In more severe cases, a dentist may prescribe stronger pain medications. Additionally, rinsing the mouth with warm salt water can help soothe the area and promote healing. Pain management is typically used in conjunction with other treatments, such as antibiotics or drainage, to address the underlying cause of the abscess. Proper pain control not only improves comfort but also aids in the overall recovery process.
Home Remedies
While certain home remedies like saltwater rinses or clove oil application can offer temporary pain relief, they’re not a substitute for professional treatment. Preventative measures such as regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups are the best defence against dental abscesses. A balanced diet and quitting tobacco also play crucial roles in maintaining oral health.
- Saltwater rinses
- Cold compresses
- Clove oil applications
Preventive Measures
Good Oral Hygiene Practices
Brushing twice daily, flossing, and using mouthwash can significantly reduce the risk of dental abscesses.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Routine visits to the dentist can help identify and address dental issues before they develop into abscesses.
Diet and Lifestyle Modifications
Limiting sugar intake and avoiding tobacco products can help maintain oral health and prevent infections.
Importance of Seeking Timely Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and ensure successful recovery from dental abscesses. Maintaining good oral hygiene and scheduling regular dental check-ups are crucial steps in preventing dental abscesses and promoting overall oral health. For more information on dental abscesses and other oral health issues, consult your dentist.