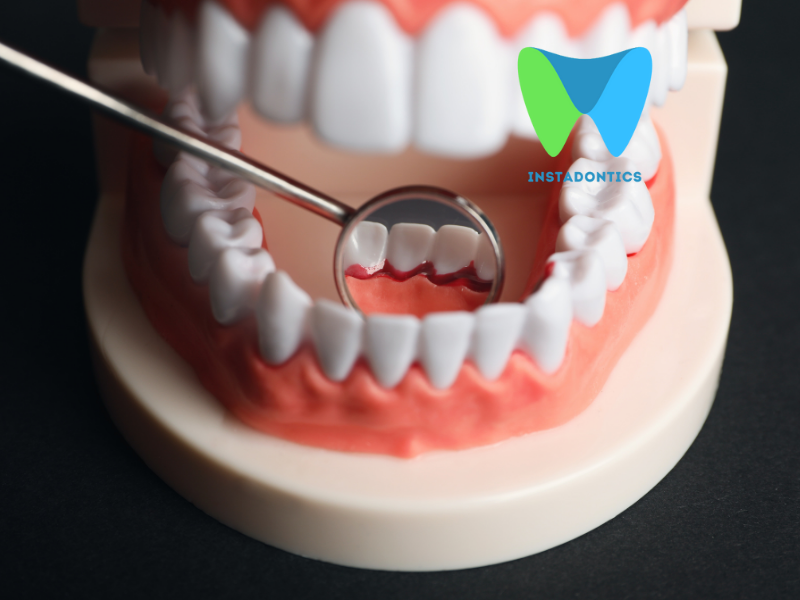
Imagine this: the clock ticks a serene morning or a quiet evening away, you’re in front of the mirror, toothbrush in hand, partaking in your habitual oral care routine. Suddenly, a faint pink swirls in the sink—a signal set off by your body, an alert not to be ignored. While prevalent, bleeding gums during brushing should never be considered normal. This phenomenon is not merely a dental concern; it’s a harbinger of possible deeper health issues. “Why do my gums bleed when I brush my teeth?” is more than a question—it’s a quest for understanding the intricacies of oral health and its impact on our overall wellbeing. In this comprehensive guide, we not only explore the root causes but also unveil actionable solutions to reclaim your gum health and, by extension, safeguard your smile.
Why Do My Gums Bleed When I Brush My Teeth | Understanding Gums
Anatomy and Role of Gums
Your gums, or gingiva, are the foundational pillars of your oral health. Comprising firm, fibrous tissue covered by mucous membrane, they snugly encase your teeth, guarding the bones and providing a seal against bacterial invasions. Healthy gums are the unsung heroes, often overlooked until a problem arises.
Gingival Bleeding: The First Red Flag
Gingival bleeding — or bleeding from the gums — signifies the first cry for help from these vital tissues. While it might be easy to brush it off as a minor irritant, understanding its root causes is critical. By addressing it timely, you dodge more profound health implications, setting the stage for lasting dental health.
Why Do My Gums Bleed When I Brush My Teeth | Unraveling the Causes of Bleeding Gums
Poor Oral Hygiene: The Primary Culprit
Inadequate brushing and neglecting to floss lead to plaque buildup—a sticky, colorless film of bacteria. If not removed, plaque hardens into tartar, inflaming the gums, causing gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease, which manifests as bleeding during brushing.
Overzealous Brushing: Doing More Harm Than Good
Think harder brushing equals cleaner teeth? Think again. An aggressive brushing technique or a toothbrush with hard bristles can wear down your gum tissue, leading to recession and bleeding.
Nutritional Deficiencies: The Diet-Gum Health Connection
Vitamins C and K are vital for gum health. A deficiency in these nutrients weakens the gum’s integrity, making them more susceptible to bleeding.
Medication Side Effects: An Unintended Consequence
Certain medications, especially those for blood thinning, can increase bleeding risk. Always review these side effects with your healthcare provider.
Underlying Health Conditions: The Bigger Picture
Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and hormonal changes during pregnancy can affect your gum health, causing bleeding during dental hygiene practices.
Why Do My Gums Bleed When I Brush My Teeth | Strategies for Prevention and Treatment
Adopting Proper Brushing Techniques
Opt for a soft-bristled brush and gently move it in circular motions to remove plaque without harming your gums. Brushing twice a day and flossing at least once is foundational to gum health.
Harnessing the Power of Flossing
Flossing isn’t just for removing food particles—it disrupts plaque colonies, preventing them from hardening into tartar. Floss gently to avoid injuring the gum line.
Continuing with the structure and guidance provided earlier, here’s how to expand on the next couple of sections to keep building your article.
Why Do My Gums Bleed When I Brush My Teeth | Home Remedies
While seeking professional dental advice is paramount for persistent bleeding gums, there are several home remedies that can aid in reducing the symptoms and improving your gum health. These practices have been passed down through generations and can often provide a natural way to fortify your gums.
Saltwater Rinses: The Classic Healer
A saltwater rinse can reduce inflammation and kill bacteria. Dissolve a teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and swish gently around the mouth for 30 seconds before spitting it out. This simple solution can be used two to three times a day to help soothe inflamed gums.
Tea Tree Oil: Nature’s Antiseptic
Tea tree oil has natural anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. Adding a drop of tea tree oil to your toothpaste, or using a tea tree oil-based toothpaste can assist in reducing gum bleeding. However, be mindful as tea tree oil can be quite potent and should never be swallowed.
Crunchy Vegetables: Nature’s Toothbrush
Incorporating crunchy vegetables like carrots and celery into your diet is not only nutritious but also helps to naturally clean your teeth and massage your gums, promoting blood circulation and health.
Stress Reduction: The Mind-Body Connection
Chronic stress can negatively impact your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off infections that cause gum disease. Incorporating stress-reducing techniques such as deep breathing, yoga, or meditation into your routine can have positive effects on your oral health.
When to See a Dentist: Recognizing the Red Flags
Knowing when to seek professional help is crucial. Some symptoms should prompt an immediate visit to the dentist:
- Persistent Bleeding: If your gums bleed regularly or excessively, it’s time to make an appointment.
- Long-term Bad Breath: Chronic bad breath can be an indicator of periodontitis, an advanced form of gum disease.
- Receding Gums: If you notice that your teeth are looking longer than usual, your gums may be receding—a sign of gum disease.
- Loose Teeth: This can indicate that the support structure of your teeth is being compromised by gum disease.
Your dentist can provide the necessary treatments and preventive strategies, such as professional cleanings, scaling, and root planing, which reach deeper into the pockets of gums to remove stubborn plaque and tartar build-up.
The Road to Recovery: Healing and Maintenance
Once you and your dentist have addressed the immediate concerns with your bleeding gums, maintaining gum health is about consistent care and regular check-ups.
Post-Treatment Care for Gum Health
After any dental treatment, follow your dentist’s instructions religiously. This might include special mouthwashes, more frequent cleanings, or specific brushing or flossing techniques.
Preventative Maintenance
Regular preventive care can stave off complications. This includes twice-daily brushing, daily flossing, using an antibacterial mouthwash, and quitting smoking if you smoke.
Regular Professional Care
Maintain regular check-ups with your dentist every six months or as recommended. Professional cleanings are crucial for removing the plaque and tartar that you cannot remove with at-home oral hygiene alone.
Bleeding gums when brushing is a condition that requires attention and should be viewed as a pivot point to take action towards better oral hygiene practices. By understanding the causes and employing a combination of home remedies, professional care, and daily preventive measures, you can heal your gums and prevent future issues. Take charge of your oral health today, and embrace a future of vibrant, healthy smiles. Your body will thank you – from top to toe.