Why Do My Teeth Hurt When I Bite Down | Tooth pain when biting down can be both a puzzling and concerning issue. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for addressing the discomfort effectively. Common reasons for this pain include cavities, cracked teeth, gum disease, and more, each linked to the sensitivity of the tooth’s structure. Identifying the specific cause can help in determining the appropriate treatment.
Many individuals experience this discomfort at some point, and it often signals a deeper dental problem that requires attention. Factors like high fillings or misalignment can also contribute to excessive pressure on the teeth, leading to pain when biting down. Taking the time to learn about these causes is essential for anyone dealing with this issue.
By exploring the various reasons behind this tooth pain, individuals can empower themselves to take action. Seeking professional dental care is often the recommended next step for effective relief, allowing individuals to maintain their oral health and comfort in everyday activities.
Common Causes of Tooth Pain
Tooth pain when biting down can stem from various dental issues. Understanding the specific causes can help in identifying the right treatment and addressing discomfort effectively.
Tooth Decay and Cavities
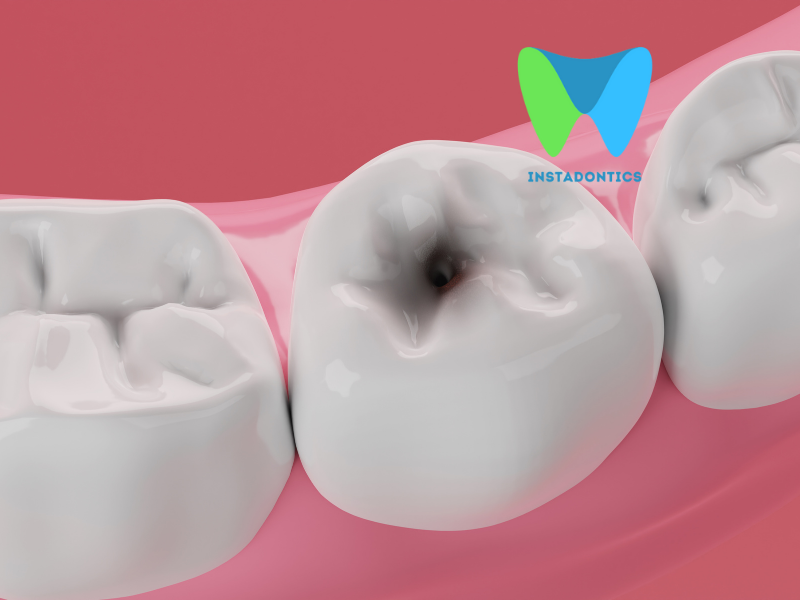
Tooth decay is one of the primary reasons for pain when biting down. When bacteria accumulate on enamel, they produce acids that erode the tooth’s outer layer, potentially leading to cavities.
As cavities develop, the inner layers of the tooth become exposed, causing sensitivity and pain during pressure. Regular dental check-ups can help identify and treat cavities early, preventing severe damage that leads to increased discomfort.
Gum Disease
Gum disease, particularly periodontitis, can also contribute to tooth pain. Inflammation and infection surrounding the teeth weaken the supporting structures.
When the gums recede, they can expose sensitive areas of the tooth, leading to pain when biting down or chewing. Preventive care, including proper oral hygiene practices and regular cleanings, can mitigate the risks associated with gum disease.
Tooth Abscess
A tooth abscess is a collection of pus caused by bacterial infection, occurring within the tooth or surrounding tissue. This condition results in significant pain, especially during biting or applying pressure.
Symptoms include swelling, redness, and sometimes fever. Timely treatment is crucial, as an abscess can lead to more serious health issues if left untreated. Dental intervention often involves draining the abscess and possibly performing a root canal.
Dental Fractures
Fractured teeth can occur due to trauma, biting hard objects, or significant decay. A fracture often leads to sharp pain when biting down, as the pressure aggravates the damaged area.
Cracks may be visible or hidden, requiring professional evaluation for diagnosis. Treatment options range from bonding and crowns to more extensive procedures based on the severity of the fracture.
Damaged Fillings or Dental Restorations
Fillings and dental restorations can wear down or become damaged over time, resulting in discomfort when biting. If a filling is loose or cracked, it may not adequately protect the tooth underneath, leading to sensitivity and pain.
Patients are advised to monitor their restorations and consult a dentist if they notice changes. Regular examinations can help identify issues with existing dental work before they escalate into more painful conditions.
Why Do My Teeth Hurt When I Bite Down
Dental Diagnosis and Examination
A thorough dental diagnosis is essential when experiencing pain while biting down. This process includes several techniques to identify the underlying causes of tooth discomfort, ensuring effective treatment options are available.
Clinical Evaluation
During a clinical evaluation, the dentist performs a comprehensive examination of the patient’s teeth and gums. This step involves visually inspecting the mouth for signs of decay, cracks, or gum disease. The dentist will also assess the alignment of the teeth.
Patients may be asked to explain their symptoms in detail, including when the pain occurs and its intensity. This information is crucial for understanding the context of the pain. Oral health history and potential risk factors, such as previous dental work, will also be discussed to help narrow down possible causes.
Dental X-Rays
Dental X-rays play a significant role in diagnosing issues that are not visible during a clinical examination. These imaging techniques allow the dentist to see the internal structure of the teeth and surrounding bone.
X-rays can reveal problems such as cavities, abscesses, or impacted teeth. They can also identify issues like the extent of decay or structural damage within a tooth. By analyzing the images, the dentist can formulate a precise diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment.
Sensitivity Tests
Sensitivity tests are employed to evaluate a tooth’s reaction to temperature changes or pressure. These tests help determine if there are issues such as nerve damage, exposed dentin, or other conditions causing discomfort.
Common methods include applying hot or cold stimuli to the tooth or using a bite stick to assess for pain when pressure is applied. The patient’s reaction provides valuable information regarding the tooth’s health. An authoritative analysis of these responses leads to a more accurate diagnosis and better-targeted treatment options.
Why Do My Teeth Hurt When I Bite Down
Treatment Options
When a person experiences discomfort while biting down, various treatment options may be available, depending on the underlying cause. The appropriate approach can involve restorative techniques, surgical interventions, or ongoing dental care tailored to the specific condition affecting the teeth.
Fillings and Repairs
When tooth decay or minor fractures cause pain while biting, dental fillings or repairs are often the first line of treatment. A dentist will remove the decayed portion of the tooth and fill it with materials such as composite resin, amalgam, or glass ionomer. These materials are designed to match the natural color of the tooth while providing strength and durability.
For small cracks, dental bonding can be used. This involves applying a tooth-colored resin to repair the damage, restoring the tooth’s integrity and function. Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent further decay or damage, ensuring longevity and comfort for the affected tooth.
Root Canal Therapy
Root canal therapy is necessary when the dental pulp becomes infected or inflamed, often leading to significant pain. During the procedure, a dentist removes the infected pulp, cleans the root canals, and seals them to prevent future infections.
After a root canal, the tooth may require a crown for added support. This procedure alleviates pain and allows the patient to retain their natural tooth, which is preferable to extraction. Individuals who undergo root canal therapy should follow post-treatment care to ensure healing and the health of the remaining tooth structure.
Gum Disease Treatment
Pain while biting can also stem from gum disease, which affects the supporting structures of the teeth. Initial treatment may include scaling and root planing, a deep-cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline.
For more advanced stages, surgical options may be necessary. This can involve flap surgery or gum grafts to restore gum health. Maintaining proper oral hygiene and regular dental checkups are essential steps to prevent gum disease, thereby reducing the risk of discomfort while biting down.
Dental Crowns and Veneers
When teeth are significantly damaged or weakened, dental crowns or veneers can provide both cosmetic and functional restoration. A crown covers the entire tooth, offering strength and protecting it from further damage. This is particularly useful after procedures like root canals.
Veneers, on the other hand, are thin shells that cover the front surface of teeth to improve appearance. They can address issues such as discoloration, chips, or slight misalignments. Both treatments improve the tooth’s structural integrity and relieve discomfort associated with biting.
Why Do My Teeth Hurt When I Bite Down
Preventive Measures
Maintaining dental health is crucial to prevent tooth pain when biting down. Effective practices include good oral hygiene, regular dental visits, and utilizing protective appliances. These measures help ensure strong teeth and healthy gums.
Oral Hygiene Practices
A consistent oral hygiene routine is essential. Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste helps remove plaque, which can lead to cavities and sensitivity. Flossing daily is equally important, as it removes debris between teeth that a toothbrush can’t reach.
Using an antibacterial mouthwash can enhance the effectiveness of brushing and flossing. This helps in reducing oral bacteria, which can contribute to gum disease and tooth decay. It’s also advisable to replace toothbrushes every three to four months or sooner if bristles fray.
Regular Dental Check-Ups
Regular visits to a dentist are vital for monitoring oral health. It is recommended to have check-ups at least every six months. During these visits, a dentist can detect issues such as cavities, gum disease, or other conditions before they worsen.
Professional cleanings remove tartar buildup that regular brushing may miss. Dentists also provide tailored advice on maintaining dental health, helping to identify risk factors early on, and ensuring timely intervention if issues arise.
Protective Dental Appliances
For those who grind their teeth or have specific dental issues, protective appliances can be beneficial. A custom night guard can prevent damage from grinding during sleep, reducing the risk of tooth wear and sensitivity.
Sports mouthguards protect teeth during physical activities, minimizing the risk of trauma. Wearing these appliances can significantly reduce discomfort associated with tooth pain when biting down, promoting overall oral health and resilience.
Why Do My Teeth Hurt When I Bite Down
When to See a Dentist
Experiencing tooth pain when biting down can be concerning. Certain symptoms signal that professional dental care may be necessary to address underlying issues effectively. Recognizing these signs can lead to timely interventions and prevent further complications.
Persistent Pain
If tooth pain persists for more than a few days, it is essential to consult a dentist. Continuous discomfort may indicate a more serious problem, such as a cracked tooth or an abscess. Ignoring this type of pain could lead to worsening conditions, potentially requiring more extensive treatment like a root canal or extraction.
Patients should note the location and intensity of the pain, as detailed information can help the dentist make a more accurate diagnosis. Consistent pain often correlates with structural damage or infection, making swift action crucial.
Increased Sensitivity to Temperature
Heightened sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks can be a significant indicator of dental issues. This sensitivity may suggest enamel erosion, gum recession, or potentially a dental cavity. If sudden temperature changes cause discomfort, a dentist should evaluate the condition.
This increased sensitivity might also be a sign of pulpitis, where the tooth’s pulp is inflamed. A thorough examination can help determine the cause and appropriate treatment, ensuring that the sensitivity is addressed before it escalates.
Pain When Chewing or Biting
Experiencing sharp pain while chewing or biting can indicate various dental problems. This type of pain might stem from a cracked tooth, a failing filling, or an unstable crown. When pressure is applied during eating, the discomfort can worsen, necessitating immediate dental attention.
It’s important for individuals to specify when the pain occurs—whether with certain foods or types of movement. Such details can greatly assist the dentist in diagnosing the issue effectively.
Swelling Around a Tooth or in the Jaw
Swelling in the gums or jaw area surrounding a specific tooth is a clear sign that dental intervention is required. This swelling may denote an infection or periodontal disease, requiring prompt treatment to prevent further complications.
In some cases, swelling can indicate an abscess or an impacted tooth. If accompanied by fever or difficulty swallowing, immediate dental care is critical. Evaluating both the swelling and associated symptoms allows for targeted treatment, reducing the risk of more severe health issues.
FAQs: Why Do My Teeth Hurt When I Bite Down?
1. Why Do My Teeth Hurt When I Bite Down?
Tooth pain when biting down is often a sign of an underlying dental issue, such as tooth decay, gum disease, a cracked tooth, or issues with dental restorations like fillings or crowns.
2. What Are Common Causes of This Pain?
- Cavities (Tooth Decay): Untreated cavities can expose the inner layers of your tooth, causing sensitivity when pressure is applied.
- Cracked or Fractured Tooth: A crack may cause pain during biting, especially if it extends into the nerve.
- Dental Abscess or Infection: An infection in the tooth or surrounding bone can lead to pain, especially with pressure.
- Gum Disease: Inflamed gums or gum recession can expose the roots, making teeth sensitive to pressure.
- Tooth Grinding (Bruxism): Chronic grinding can wear down enamel and irritate the tooth’s nerve.
- High Filling or Crown: A dental restoration that is too high can create uneven bite pressure, leading to pain.
3. How Can I Tell If the Pain Is Serious?
- Pain that persists, worsens, or is accompanied by swelling, fever, or redness may indicate an infection and requires immediate dental care.
- Localized pain when biting on a specific tooth could mean a crack or abscess that needs attention.
4. Why Does My Tooth Hurt Even After a Filling or Crown?
After dental work, it’s normal to have mild sensitivity, but prolonged or sharp pain when biting may suggest:
- A misaligned bite.
- An incomplete seal on the filling or crown.
- Residual nerve irritation or inflammation.
5. What Should I Do If My Tooth Hurts When Biting Down?
- Avoid chewing on the affected side.
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers as directed for temporary relief.
- Apply a cold compress if swelling occurs.
- Schedule a dental appointment to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
6. How Is This Pain Treated?
- Cavities: Fillings or root canals may be needed.
- Cracked Tooth: Bonding, crowns, or extractions might be required, depending on the crack’s severity.
- Infections: Antibiotics, drainage, or root canal therapy may be necessary.
- Grinding: Nightguards can help reduce pressure on your teeth.
7. Can I Prevent Tooth Pain When Biting?
- Practice excellent oral hygiene to prevent cavities and gum disease.
- Wear a nightguard if you grind your teeth.
- Avoid using your teeth to bite down on hard objects like ice or pens.
- Visit your dentist regularly for checkups to catch problems early.
8. When Should I See a Dentist?
- If the pain is severe, persistent, or worsens over time.
- If biting causes sharp or throbbing pain.
- If you notice swelling, pus, or changes in the tooth’s color.
Addressing tooth pain early ensures better outcomes and prevents more serious complications.